Page 715 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 715
688 Part SIX Systemic Immune Diseases
Progression of autoimmunity may dictate autospecificity (as above) but is less important in
determining risk of disease.
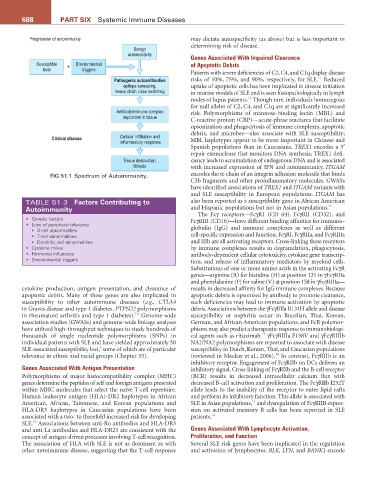
Benign
autoreactivity
Genes Associated With Impaired Clearance
Susceptible + Environmental of Apoptotic Debris
host triggers
Patients with severe deficiencies of C2, C4, and C1q display disease
11
Pathogenic autoantibodies risks of 10%, 75%, and 90%, respectively, for SLE. Reduced
epitope spreading, uptake of apoptotic cells has been implicated in disease initiation
heavy chain class switching in murine models of SLE and is seen histopathologically in lymph
12
nodes of lupus patients. Though rare, individuals homozygous
for null alleles of C2, C4, and C1q are at significantly increased
Antibody/immune complex risk. Polymorphisms of mannose-binding lectin (MBL) and
deposition in tissue
C-reactive protein (CRP)—acute-phase reactants that facilitate
opsonization and phagocytosis of immune complexes, apoptotic
debris, and microbes—also associate with SLE susceptibility;
Clinical disease Cellular infiltration and MBL haplotypes appear to be more important in Chinese and
inflammatory response
Spanish populations than in Caucasians. TREX1 encodes a 3′
repair exonuclease that monitors DNA synthesis; TREX1 defi-
Tissue destruction, ciency leads to accumulation of endogenous DNA and is associated
fibrosis with increased expression of IFN and autoimmunity. ITGAM
FIG 51.1 Spectrum of Autoimmunity. encodes the α-chain of an integrin adhesion molecule that binds
C3b fragments and other proinflammatory molecules. GWASs
have identified associations of TREX1 and ITGAM variants with
and SLE susceptibility in European populations. ITGAM has
TABLE 51.3 Factors Contributing to also been reported as a susceptibility gene in African American
9
autoimmunity and Hispanic populations but not in Asian populations.
The Fcγ receptors—FcγR1 (CD 64), FcγRII (CD32), and
• Genetic factors FcγRIII (CD16)—have different binding affinities for immuno-
• Loss of peripheral tolerance
• B-cell abnormalities globulin (IgG) and immune complexes as well as different
• T-cell abnormalities cell-specific expression and function. FcγRI, FcγRIIa, and FcγRIIIa
• Dendritic cell abnormalities and IIIb are all activating receptors. Cross-linking these receptors
• Cytokine milieu by immune complexes results in degranulation, phagocytosis,
• Hormonal influences antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity, cytokine gene transcrip-
• Environmental triggers tion, and release of inflammatory mediators by myeloid cells.
Substitutions of one or more amino acids in the activating FcγR
genes—arginine (R) for histidine (H) at position 131 in γFcγRIIa
and phenylalanine (F) for valine (V) at position 158 in γFcγRIIIa—
cytokine production, antigen presentation, and clearance of results in decreased affinity for IgG immune complexes. Because
apoptotic debris. Many of these genes are also implicated in apoptotic debris is opsonized by antibody to promote clearance,
susceptibility to other autoimmune diseases (e.g., CTLA4 such deficiencies may lead to immune activation by apoptotic
in Graves disease and type 1 diabetes, PTPN22 polymorphisms debris. Associations between the γFcγRIIa R131H allele and disease
7,8
in rheumatoid arthritis and type 1 diabetes). Genome-wide susceptibility or nephritis occur in Brazilian, Thai, Korean,
association studies (GWASs) and genome-wide linkage analyses German, and African American populations, and FcR polymor-
have utilized high-throughput techniques to study hundreds of phisms may also predict a therapeutic response to immunobiologi-
13
thousands of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in cal agents such as rituximab. γFcγRIIIa F158V and γFcγRIIIb
individual patients with SLE and have yielded approximately 50 NA2/NA2 polymorphisms are reported to associate with disease
9
SLE-associated susceptibility loci, some of which are of particular susceptibility in Dutch, Korean, Thai, and Caucasian populations
14
relevance in ethnic and racial groups (Chapter 33). (reviewed in Mackay et al., 2006). In contrast, FcγRIIb is an
inhibitory receptor. Engagement of FcγRIIb on DCs delivers an
Genes Associated With Antigen Presentation inhibitory signal. Cross-linking of FcγRIIb and the B-cell receptor
Polymorphisms of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) (BCR) results in decreased intracellular calcium flux with
genes determine the peptides of self and foreign antigens presented decreased B-cell activation and proliferation. The FcγRIIb I232T
within MHC molecules that select the naïve T-cell repertoire. allele leads to the inability of the receptor to enter lipid rafts
Human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-DR2 haplotypes in African and perform its inhibitory function. This allele is associated with
15
American, African, Taiwanese, and Korean populations and SLE in Asian populations, and dysregulation of FcγRIIB expres-
HLA-DR3 haplotypes in Caucasian populations have been sion on activated memory B cells has been reported in SLE
associated with a two- to threefold increased risk for developing patients. 14
10
SLE. Associations between anti-Ro antibodies and HLA-DR3
and anti-La antibodies and HLA-DR25 are consistent with the Genes Associated With Lymphocyte Activation,
concept of antigen-driven processes involving T-cell recognition. Proliferation, and Function
The association of HLA with SLE is not as dominant as with Several SLE risk genes have been implicated in the regulation
other autoimmune disease, suggesting that the T-cell response and activation of lymphocytes. BLK, LYN, and BANK1 encode