Page 765 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 765
CHaPTEr 54 Sjögren Syndrome 737
CLiNiCaL PEarLS
• Chronic fatigue is a prominent presenting feature of Sjögren syndrome
(SS).
• Autonomic nervous system involvement and peripheral nervous system
involvement are often underrecognized.
• Mimics of SS include immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4)–related disease
(Mikulicz disease), hepatitis C infection, sarcoidosis, and human
T-lymphotropic virus (HTLV) infection.
• Presence of joint erosions and complement control protein (CCP)
antibody is indicative of secondary SS caused by rheumatoid
arthritis.
• Prolonged use of topical ophthalmic nonsteroidal antiinflammatory
drugs (NSAIDs) and steroid preparations should be avoided to reduce
the risk for local complications.
• Sudden normalization of previously elevated rheumatoid factor should
prompt evaluation for development of lymphoma.
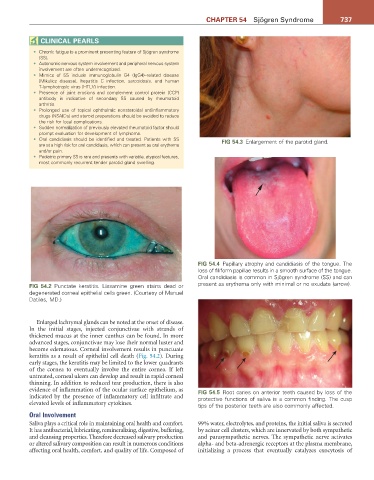
• Oral candidiasis should be identified and treated. Patients with SS FiG 54.3 Enlargement of the parotid gland.
are at a high risk for oral candidiasis, which can present as oral erythema
and/or pain.
• Pediatric primary SS is rare and presents with variable, atypical features,
most commonly recurrent tender parotid gland swelling.
FiG 54.4 Papillary atrophy and candidiasis of the tongue. The
loss of filiform papillae results in a smooth surface of the tongue.
Oral candidiasis is common in Sjögren syndrome (SS) and can
FiG 54.2 Punctate keratitis. Lissamine green stains dead or present as erythema only with minimal or no exudate (arrow).
degenerated corneal epithelial cells green. (Courtesy of Manuel
Datiles, MD.)
Enlarged lachrymal glands can be noted at the onset of disease.
In the initial stages, injected conjunctivae with strands of
thickened mucus at the inner canthus can be found. In more
advanced stages, conjunctivae may lose their normal luster and
become edematous. Corneal involvement results in punctuate
keratitis as a result of epithelial cell death (Fig. 54.2). During
early stages, the keratitis may be limited to the lower quadrants
of the cornea to eventually involve the entire cornea. If left
untreated, corneal ulcers can develop and result in rapid corneal
thinning. In addition to reduced tear production, there is also
evidence of inflammation of the ocular surface epithelium, as FiG 54.5 Root caries on anterior teeth caused by loss of the
indicated by the presence of inflammatory cell infiltrate and protective functions of saliva is a common finding. The cusp
elevated levels of inflammatory cytokines. tips of the posterior teeth are also commonly affected.
Oral Involvement
Saliva plays a critical role in maintaining oral health and comfort. 99% water, electrolytes, and proteins, the initial saliva is secreted
It has antibacterial, lubricating, remineralizing, digestive, buffering, by acinar cell clusters, which are innervated by both sympathetic
and cleansing properties. Therefore decreased salivary production and parasympathetic nerves. The sympathetic nerve activates
or altered salivary composition can result in numerous conditions alpha- and beta-adrenergic receptors at the plasma membrane,
affecting oral health, comfort, and quality of life. Composed of initializing a process that eventually catalyzes exocytosis of