Page 875 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 875
CHaPter 62 Immunohematological Disorders 847
(haptoglobin, hemopexin, albumin), resulting in hemoglobinuria. Antibody-coated red cells from patient Reagent anti-IgG
Because hemoglobin is toxic to the renal tubular epithelium,
renal function may become impaired. RBC membrane fragments
released by massive intravascular hemolysis are a rich source of
procoagulant phosphatidylserine and can precipitate disseminated
intravascular coagulation. +
In contrast, the consequences of extravascular hemolysis (i.e.,
via phagocytosis in the reticuloendothelial system of the liver
and the spleen) are much less severe. In macrophages, iron is
removed from the hemoglobin and recycled to the circulation
to support a compensatory reticulocytosis and the heme porphyrin
is metabolized to bilirubin.
Patients with immune-mediated anemia have an increased
incidence of venous thromboembolism, and detection of a lupus Visible red cell agglutination
anticoagulant in these patients places them at a particularly high
risk for this complication. 14
Diagnosis
With few exceptions, if the mechanism of hemolysis is immune
mediated, an anti-RBC antibody can be demonstrated, either
1,2
on the RBC surface, in serum, or both. With autoimmune
hemolysis, IgG or IgM and/or complement components can be
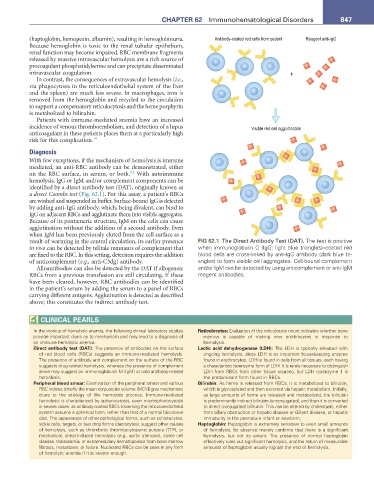
identified by a direct antibody test (DAT), originally known as
a direct Coombs test (Fig. 62.1). For this assay, a patient’s RBCs
are washed and suspended in buffer. Surface-bound IgG is detected
by adding anti-IgG antibody, which, being divalent, can bind to
IgG on adjacent RBCs and agglutinate them into visible aggregates.
Because of its pentameric structure, IgM on the cells can cause
agglutination without the addition of a second antibody. Even
when IgM has been previously eluted from the cell surface as a
result of warming in the central circulation, its earlier presence FIG 62.1 The Direct Antibody Test (DAT). The test is positive
in vivo can be detected by telltale remnants of complement that when immunoglobulin G (IgG: light blue triangles)–coated red
are fixed to the RBC. In this setting, detection requires the addition blood cells are cross-linked by anti-IgG antibody (dark blue tri-
of anticomplement (e.g., anti-C3dg) antibody. angles) to form visible cell aggregates. Cell-bound complement
Alloantibodies can also be detected by the DAT if allogeneic and/or IgM can be detected by using anticomplement or anti-IgM
RBCs from a previous transfusion are still circulating. If these reagent antibodies.
have been cleared, however, RBC antibodies can be identified
in the patient’s serum by adding the serum to a panel of RBCs
carrying different antigens. Agglutination is detected as described
above; this constitutes the indirect antibody test.
CLInICaL PearLS
In the workup of hemolytic anemia, the following clinical laboratory studies reticulocytes: Evaluation of the reticulocyte count indicates whether bone
provide important clues as to mechanism and may lead to a diagnosis of marrow is capable of making new erythrocytes in response to
an immune hemolytic anemia. hemolysis.
Direct antibody test (Dat): The presence of antibodies on the surface Lactic acid dehydrogenase (LDH): The LDH is typically elevated with
of red blood cells (RBCs) suggests an immune-mediated hemolysis. ongoing hemolysis, since LDH is an important housekeeping enzyme
The presence of antibody and complement on the surface of the RBC found in erythrocytes. LDH is found in cells from all tissues, each having
suggests drug-related hemolysis, whereas the presence of complement a characteristic isoenzyme form of LDH. It is rarely necessary to distinguish
alone may suggest an immunoglobulin M (IgM) or cold antibody-related LDH from RBCs from other tissue sources, but LDH isoenzyme 1 is
hemolysis. the predominant form found in RBCs.
Peripheral blood smear: Examination of the peripheral smear and various Bilirubin: As heme is released from RBCs, it is metabolized to bilirubin,
RBC indices (chiefly the mean corpuscular volume [MCV]) give mechanistic which is glycosylated and then excreted via hepatic metabolism. Initially,
clues to the etiology of the hemolytic process. Immune-mediated as large amounts of heme are released and metabolized, the bilirubin
hemolysis is characterized by spherocytosis, even microspherocytosis is predominantly indirect bilirubin (unconjugated), and then it is converted
in severe cases, as antibody-coated RBCs traversing the reticuloendothelial to direct (conjugated) bilirubin. This can be altered by cholestasis, either
system assume a spherical form, rather than that of a normal biconcave from biliary obstruction or hepatic disease or Gilbert disease, or hepatic
disc. The appearance of other pathological forms, such as schistocytes, immaturity in the premature infant or newborn.
sickle cells, targets, or tear drop forms (dacrocytes), suggest other causes Haptoglobin: Haptoglobin is extremely sensitive to even small amounts
of hemolysis, such as thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP), or of hemolysis. Its absence merely confirms that there is a significant
mechanical, shear-induced hemolysis (e.g., aortic stenosis), sickle cell hemolysis, but not its extent. The presence of normal haptoglobin
disease, thalassemia, or extramedullary hematopoiesis from bone marrow effectively rules out significant hemolysis, and the return of measurable
fibrosis, metastasis, or failure. Nucleated RBCs can be seen in any form amounts of haptoglobin usually signals the end of hemolysis.
of hemolytic anemia if it is severe enough.