Page 904 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 904
874 Part SEVEN Organ-Specific Inflammatory Disease
NF-NB NF-NB
AP1 AP1
STAT1 STAT1
STAT3 STAT3
p38
Trigger factors: p38 Erk 1/2
Pathogens Erk 1/2
Drugs
Stress
PMN
PMN PMN PMN PMN
autoantigens PMN PMN
K17, K13 LL-37 LL-37 growth signals
LL-37/ ?viral antigens? TGF-α, KGF
IL-19, IL-20
DNA
VEGF CD8 amphiregulin
DNA-LL-37 Tc1
DNA-LL-37 Endothelium TNF-α CD8 HLA-DR IL-1
RNA-LL-37 TNF-α Tc1
IFN-α KGF, FGF10
pDC CX3CL1, CCL17 GM-CSF
pDC ICAM-1, VCAM, Th1 INF-γ ICAM-1 IL-36
E-selectin
RNA-LL-37 Th17 Th1 Th22 Tc1 cytokines
RNA-LL-37 Th1 chemokines
pDC mDC Th17 Th17 Th2 CXCL10-9-11, TGF-α, GM-CSF,
Chemerin IFN-α TNF-α, IFN-γ, IL-1, IL-6,
IFN-α IL-17, IL-22 CCL2, CXCL8, IL-19, IL-20, IL-36
CCL20
Fibroblasts TIP-DC CCL5, CCL19
Endothelial cells Th1 Th17
Th17 Th2
PMN Th22
Chemerin Mast cell mDC Th1 Th2
Th17 Fibroblasts
Chemerin Th1 Mast cell Th1
Fibroblasts PMN PMN Th17 Endothelium
NK PMN
Fibroblasts
SlanDC ICAM-1, VCAM,
A B C SlanDC E-selectin
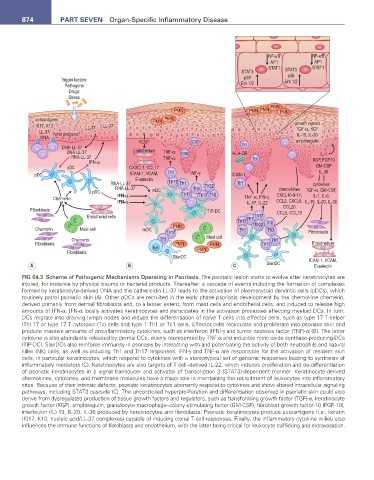
FIG 64.3 Scheme of Pathogenic Mechanisms Operating in Psoriasis. The psoriatic lesion starts to evolve after keratinocytes are
injured, for instance by physical trauma or bacterial products. Thereafter, a cascade of events including the formation of complexes
formed by keratinocyte-derived DNA and the cathelicidin LL-37 leads to the activation of plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs), which
routinely patrol psoriatic skin (A). Other pDCs are recruited in the early phase psoriasis development by the chemokine chemerin,
derived primarily from dermal fibroblasts and, to a lesser extent, from mast cells and endothelial cells, and induced to release high
amounts of IFN-α. IFN-α locally activates keratinocytes and participates in the activation processes affecting myeloid DCs. In turn,
DCs migrate into draining lymph nodes and induce the differentiation of naïve T cells into effector cells, such as type 17 T-helper
(Th) 17 or type 17 T cytotoxic (Tc) cells and type 1 Th1 or Tc1 cells. Effector cells recirculate and proliferate into psoriatic skin and
produce massive amounts of proinflammatory cytokines, such as interferon (IFN)-γ and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α (B). The latter
cytokine is also abundantly released by dermal DCs, mainly represented by TNF-α and inducible nitric oxide synthase-producing-DCs
(TIP-DC). SlanDCs also reinforce immunity in psoriasis by interacting with and potentiating the activity of both neutrophils and natural
killer (NK) cells, as well as inducing Th1 and Th17 responses. IFN-γ and TNF-α are responsible for the activation of resident skin
cells, in particular keratinocytes, which respond to cytokines with a stereotypical set of genomic responses leading to synthesis of
inflammatory mediators (C). Keratinocytes are also targets of T cell–derived IL-22, which induces proliferation and de-differentiation
of psoriatic keratinocytes in a signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3)-dependent manner. Keratinocyte-derived
chemokines, cytokines, and membrane molecules have a major role in maintaining the recruitment of leukocytes into inflammatory
sites. Because of their intrinsic defects, psoriatic keratinocytes aberrantly respond to cytokines and show altered intracellular signaling
pathways, including STAT3 cascade (C). The uncontrolled hyperproliferation and differentiation observed in psoriatic skin could also
derive from dysregulated production of tissue growth factors and regulators, such as transforming growth factor (TGF)-α, keratinocyte
growth factor (KGF), amphiregulin, granulocyte macrophage–colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), fibroblast growth factor-10 (FGF-10),
interleukin (IL)-19, IL-20, IL-36 produced by keratinocytes and fibroblasts. Psoriatic keratinocytes produce autoantigens (i.e., keratin
(K)17, K13, nucleic acid/LL-37 complexes) capable of inducing clonal T-cell responses. Finally, the inflammatory cytokine milieu also
influences the immune functions of fibroblasts and endothelium, with the latter being critical for leukocyte trafficking and extravasation.