Page 929 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 929
CHaPter 66 Multiple Sclerosis 897
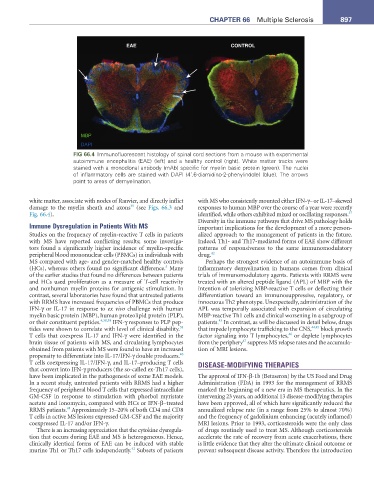
EAE CONTROL
MBP
DAPI
FIG 66.4 Immunofluorescent histology of spinal cord sections from a mouse with experimental
autoimmune encephalitis (EAE) (left) and a healthy control (right). White matter tracks were
stained with a monoclonal antibody (mAb) specific for myelin basic protein (green). The nuclei
of inflammatory cells are stained with DAPI (4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole) (blue). The arrows
point to areas of demyelination.
white matter, associate with nodes of Ranvier, and directly inflict with MS who consistently mounted either IFN-γ– or IL-17–skewed
35
damage to the myelin sheath and axons (see Figs. 66.3 and responses to human MBP over the course of a year were recently
37
Fig. 66.4). identified, while others exhibited mixed or oscillating responses.
Diversity in the immune pathways that drive MS pathology holds
Immune Dysregulation in Patients With MS important implications for the development of a more person-
Studies on the frequency of myelin-reactive T cells in patients alized approach to the management of patients in the future.
with MS have reported conflicting results; some investiga- Indeed, Th1- and Th17-mediated forms of EAE show different
tors found a significantly higher incidence of myelin-specific patterns of responsiveness to the same immunomodulatory
peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) in individuals with drug. 42
MS compared with age- and gender-matched healthy controls Perhaps the strongest evidence of an autoimmune basis of
5
(HCs), whereas others found no significant difference. Many inflammatory demyelination in humans comes from clinical
of the earlier studies that found no differences between patients trials of immunomodulatory agents. Patients with RRMS were
and HCs used proliferation as a measure of T-cell reactivity treated with an altered peptide ligand (APL) of MBP with the
and nonhuman myelin proteins for antigenic stimulation. In intention of tolerizing MBP-reactive T cells or deflecting their
contrast, several laboratories have found that untreated patients differentiation toward an immunosuppressive, regulatory, or
with RRMS have increased frequencies of PBMCs that produce innocuous Th2 phenotype. Unexpectedly, administration of the
IFN-γ or IL-17 in response to ex vivo challenge with human APL was temporally associated with expansion of circulating
myelin basic protein (MBP), human proteolipid protein (PLP), MBP-reactive Th1 cells and clinical worsening in a subgroup of
43
or their constituent peptides. 4,38,39 IFN-γ responses to PLP pep- patients. In contrast, as will be discussed in detail below, drugs
38
tides were shown to correlate with level of clinical disability. that impede lymphocyte trafficking to the CNS, 44,45 block growth
46
T cells that coexpress IL-17 and IFN-γ were identified in the factor signaling into T lymphocytes, or deplete lymphocytes
47
brain tissue of patients with MS, and circulating lymphocytes from the periphery suppress MS relapse rates and the accumula-
obtained from patients with MS were found to have an increased tion of MRI lesions.
40
propensity to differentiate into IL-17/IFN-γ double producers.
T cells coexpressing IL-17/IFN-γ, and IL-17–producing T cells DISEASE-MODIFYING THERAPIES
that convert into IFN-γ producers (the so-called ex-Th17 cells),
have been implicated in the pathogenesis of some EAE models. The approval of IFN-β-1b (Betaseron) by the US Food and Drug
In a recent study, untreated patients with RRMS had a higher Administration (FDA) in 1993 for the management of RRMS
frequency of peripheral blood T cells that expressed intracellular marked the beginning of a new era in MS therapeutics. In the
GM-CSF in response to stimulation with phorbol myristate intervening 23 years, an additional 13 disease-modifying therapies
acetate and ionomycin, compared with HCs or IFN-β–treated have been approved, all of which have significantly reduced the
41
RRMS patients. Approximately 15–20% of both CD4 and CD8 annualized relapse rate (in a range from 25% to almost 70%)
T cells in active MS lesions expressed GM-CSF and the majority and the frequency of gadolinium enhancing (acutely inflamed)
coexpressed IL-17 and/or IFN-γ. MRI lesions. Prior to 1993, corticosteroids were the only class
There is an increasing appreciation that the cytokine dysregula- of drugs routinely used to treat MS. Although corticosteroids
tion that occurs during EAE and MS is heterogeneous. Hence, accelerate the rate of recovery from acute exacerbations, there
clinically identical forms of EAE can be induced with stable is little evidence that they alter the ultimate clinical outcome or
42
murine Th1 or Th17 cells independently. Subsets of patients prevent subsequent disease activity. Therefore the introduction