Page 982 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 982
948 ParT SEvEN Organ-Specific Inflammatory Disease
PTPN22 IFIH1 SCGB3A2 TG CD25 CD40
FCRL3 CTLA4 MHC PD-L1 TSH-R BACH2
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10111213141516171819202122X Y
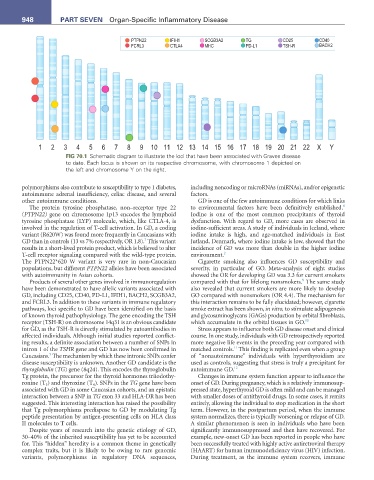
FIG 70.1 Schematic diagram to illustrate the loci that have been associated with Graves disease
to date. Each locus is shown on its respective chromosome, with chromosome 1 depicted on
the left and chromosome Y on the right.
polymorphisms also contribute to susceptibility to type 1 diabetes, including noncoding or microRNAs (miRNAs), and/or epigenetic
autoimmune adrenal insufficiency, celiac disease, and several factors.
other autoimmune conditions. GD is one of the few autoimmune conditions for which links
8
The protein tyrosine phosphatase, non–receptor type 22 to environmental factors have been definitively established.
(PTPN22) gene on chromosome 1p13 encodes the lymphoid Iodine is one of the most common precipitants of thyroid
tyrosine phosphatase (LYP) molecule, which, like CTLA4, is dysfunction. With regard to GD, more cases are observed in
involved in the regulation of Tcell activation. In GD, a coding iodinesufficient areas. A study of individuals in Iceland, where
variant (R620W) was found more frequently in Caucasians with iodine intake is high, and agematched individuals in East
7
GD than in controls (13 vs 7% respectively, OR 1.8). This variant Jutland, Denmark, where iodine intake is low, showed that the
results in a shortlived protein product, which is believed to alter incidence of GD was more than double in the higher iodine
Tcell receptor signaling compared with the wildtype protein. environment. 2
The PTPN22*620 W variant is very rare in nonCaucasian Cigarette smoking also influences GD susceptibility and
populations, but different PTPN22 alleles have been associated severity, in particular of GO. Metaanalysis of eight studies
with autoimmunity in Asian cohorts. showed the OR for developing GD was 3.3 for current smokers
9
Products of several other genes involved in immunoregulation compared with that for lifelong nonsmokers. The same study
have been demonstrated to have allelic variants associated with also revealed that current smokers are more likely to develop
GD, including CD25, CD40, PDL1, IFIH1, BACH2, SCGB3A2, GO compared with nonsmokers (OR 4.4). The mechanism for
and FCRL3. In addition to these variants in immune regulatory this interaction remains to be fully elucidated; however, cigarette
pathways, loci specific to GD have been identified on the basis smoke extract has been shown, in vitro, to stimulate adipogenesis
of known thyroid pathophysiology. The gene encoding the TSH and glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) production by orbital fibroblasts,
receptor (TSHR) on chromosome 14q31 is an obvious candidate which accumulate in the orbital tissues in GO. 10
for GD, as the TSHR is directly stimulated by autoantibodies in Stress appears to influence both GD disease onset and clinical
affected individuals. Although initial studies reported conflict course. In one study, individuals with GD retrospectively reported
ing results, a definite association between a number of SNPs in more negative life events in the preceding year compared with
11
intron 1 of the TSHR gene and GD has now been confirmed in matched controls. This finding is replicated even when a group
5
Caucasians. The mechanism by which these intronic SNPs confer of “nonautoimmune” individuals with hyperthyroidism are
disease susceptibility is unknown. Another GD candidate is the used as controls, suggesting that stress is truly a precipitant for
thyroglobulin (TG) gene (8q24). This encodes the thyroglobulin autoimmune GD. 12
Tg protein, the precursor for the thyroid hormones triiodothy Changes in immune system function appear to influence the
ronine (T 3 ) and thyroxine (T 4 ). SNPs in the TG gene have been onset of GD. During pregnancy, which is a relatively immunosup
associated with GD in some Caucasian cohorts, and an epistatic pressed state, hyperthyroid GD is often mild and can be managed
interaction between a SNP in TG exon 33 and HLADR has been with smaller doses of antithyroid drugs. In some cases, it remits
suggested. This interesting interaction has raised the possibility entirely, allowing the individual to stop medication in the short
that Tg polymorphisms predispose to GD by modulating Tg term. However, in the postpartum period, when the immune
peptide presentation by antigenpresenting cells on HLA class system normalizes, there is typically worsening or relapse of GD.
II molecules to T cells. A similar phenomenon is seen in individuals who have been
Despite years of research into the genetic etiology of GD, significantly immunosuppressed and then have recovered. For
30–40% of the inherited susceptibility has yet to be accounted example, newonset GD has been reported in people who have
for. This “hidden” heredity is a common theme in genetically been successfully treated with highly active antiretroviral therapy
complex traits, but it is likely to be owing to rare genomic (HAART) for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection.
variants, polymorphisms in regulatory DNA sequences, During treatment, as the immune system recovers, immune