Page 1343 - Hall et al (2015) Principles of Critical Care-McGraw-Hill
P. 1343
916 PART 8: Renal and Metabolic Disorders
CHAPTER Acute Kidney Injury of acute renal failure and the emergence of evidence that even small
increases in serum creatinine are associated with increased mortality
97 Claire Hannon has led to widespread adoption of diagnostic criteria for the term acute
kidney injury (AKI). AKI has largely replaced the term acute renal
2
Patrick T. Murray
failure (ARF). It is a syndrome that includes minor degrees of injury as
well as more severe renal failure, and does not allude to the mechanism
of injury. Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) is the best measure of kidney
function, but is not easily measured in clinical practice. A change in
KEY POINTS
serum creatinine or urine output is used as a marker for a change in GFR
• Prerenal azotemia and acute tubular necrosis account for the over- and forms the basis for the various diagnostic criteria for AKI.
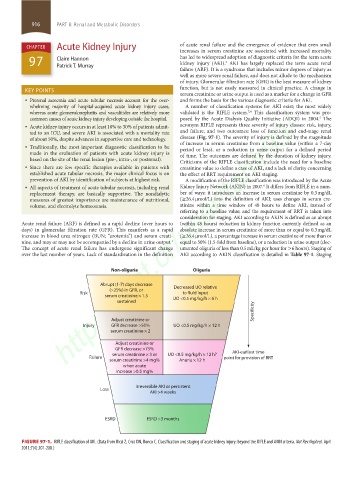
whelming majority of hospital-acquired acute kidney injury cases, A number of classification systems for AKI exist; the most widely
https://kat.cr/user/tahir99/
whereas acute glomerulonephritis and vasculitides are relatively more validated is the RIFLE system. This classification system was pro-
3,4
5
common causes of acute kidney injury developing outside the hospital. posed by the Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative (ADQI) in 2004. The
• Acute kidney injury occurs in at least 10% to 30% of patients admit- acronym RIFLE represents three severity of injury classes: risk, injury,
ted to an ICU, and severe AKI is associated with a mortality rate and failure, and two outcomes: loss of function and end-stage renal
of about 50%, despite advances in supportive care and technology. disease (Fig. 97-1). The severity of injury is defined by the magnitude
• Traditionally, the most important diagnostic classification to be of increase in serum creatinine from a baseline value (within a 7-day
period or less), or a reduction in urine output for a defined period
made in the evaluation of patients with acute kidney injury is of time. The outcomes are defined by the duration of kidney injury.
based on the site of the renal lesion (pre-, intra-, or postrenal). Criticisms of the RIFLE classification include the need for a baseline
• Since there are few specific therapies available in patients with creatinine value to define a case of AKI, and a lack of clarity concerning
established acute tubular necrosis, the major clinical focus is on the effect of RRT requirement on AKI staging.
prevention of AKI by identification of subjects at highest risk. A modification of the RIFLE classification was introduced by the Acute
6
• All aspects of treatment of acute tubular necrosis, including renal Kidney Injury Network (AKIN) in 2007. It differs from RIFLE in a num-
replacement therapy, are basically supportive. The nondialytic ber of ways: it introduces an increase in serum creatinine by 0.3 mg/dL
measures of greatest importance are maintenance of nutritional, (≥26.4 µmol/L) into the definition of AKI; uses changes in serum cre-
volume, and electrolyte homeostasis. atinine within a time window of 48 hours to define AKI, instead of
referring to a baseline value; and the requirement of RRT is taken into
consideration for staging. AKI according to AKIN is defined as an abrupt
Acute renal failure (ARF) is defined as a rapid decline (over hours to (within 48 hours) reduction in kidney function currently defined as an
days) in glomerular filtration rate (GFR). This manifests as a rapid absolute increase in serum creatinine of more than or equal to 0.3 mg/dL
increase in blood urea nitrogen (BUN; “azotemia”) and serum creati- (≥26.4 µmol/L), a percentage increase in serum creatinine of more than or
nine, and may or may not be accompanied by a decline in urine output. equal to 50% (1.5-fold from baseline), or a reduction in urine output (doc-
1
The concept of acute renal failure has undergone significant change umented oliguria of less than 0.5 mL/kg per hour for >6 hours). Staging of
over the last number of years. Lack of standardization in the definition AKI according to AKIN classification is detailed in Table 97-1. Staging
Non-oliguria Oliguria
Abrupt (1-7) days decrease Decreased UO relative
(>25%) in GFR, or
Risk to fluid input
serum creatinine × 1.5 UO <0.5 mg/kg/h × 6 h
sustained
Specificity
Adjust creatinine or
Injury GFR decrease >50% UO <0.5 mg/kg/h × 12 h
serum creatinine × 2
Adjust creatinine or
GFR decrease >75%
serum creatinine × 3 or UO <0.5 mg/kg/h × 12 h? AKI-earliest time
Failure point for provision of RRT
serum creatinine >4 mg% Anuria × 12 h
when acute
increase >0.5 mg%
Irreversible AKI or persistent
Loss
AKI >4 weeks
ESRD ESRD >3 months
FIGURE 97-1. RIFLE classification of AKI. (Data from Ricci Z, Cruz DN, Ronco C. Classification and staging of acute kidney injury: beyond the RIFLE and AKIN criteria. Nat Rev Nephrol. April
2011;7(4):201-208.)
section08.indd 916 1/14/2015 8:27:52 AM