Page 1466 - Hall et al (2015) Principles of Critical Care-McGraw-Hill
P. 1466
CHAPTER 104: Jaundice, Diarrhea, Obstruction, and Pseudoobstruction 1005
obstipation, bloating) can make the diagnosis, and history of previous
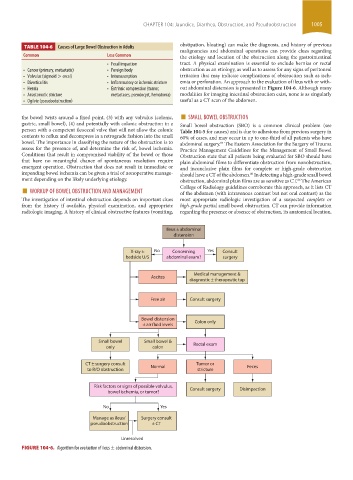
TABLE 104-6 Causes of Large Bowel Obstruction in Adults
malignancies and abdominal operations can provide clues regarding
Common Less Common the etiology and location of the obstruction along the gastrointestinal
• Fecal impaction tract. A physical examination is essential to exclude hernias or rectal
• Cancer (primary, metastatic) • Foreign body obstruction as an etiology, as well as to assess for any signs of peritoneal
• Volvulus (sigmoid > cecal) • Intussusception irritation that may indicate complications of obstruction such as isch-
• Diverticulitis • Inflammatory or ischemic stricture emia or perforation. An approach to the evaluation of ileus with or with-
• Hernia • Extrinsic compression (tumor, out abdominal distension is presented in Figure 104-6. Although many
• Anastomotic stricture metastases, pseudocyst, hematoma) modalities for imaging intestinal obstruction exist, none is as singularly
• Ogilvie (pseudoobstruction) useful as a CT scan of the abdomen.
■
the bowel twists around a fixed point, (3) with any volvulus (colonic, SMALL BOWEL OBSTRUCTION
gastric, small bowel), (4) and potentially with colonic obstruction in a Small bowel obstruction (SBO) is a common clinical problem (see
person with a competent ileocecal valve that will not allow the colonic Table 104-5 for causes) and is due to adhesions from previous surgery in
contents to reflux and decompress in a retrograde fashion into the small 60% of cases, and may occur in up to one-third of all patients who have
bowel. The importance in classifying the nature of the obstruction is to abdominal surgery. The Eastern Association for the Surgery of Trauma
85
assess for the presence of, and determine the risk of, bowel ischemia. Practice Management Guidelines for the Management of Small Bowel
Conditions that result in compromised viability of the bowel or those Obstruction state that all patients being evaluated for SBO should have
that have no meaningful chance of spontaneous resolution require plain abdominal films to differentiate obstruction from nonobstruction,
emergent operation. Obstruction that does not result in immediate or and inconclusive plain films for complete or high-grade obstruction
impending bowel ischemia can be given a trial of nonoperative manage- should have a CT of the abdomen. In detecting a high-grade small bowel
86
ment depending on the likely underlying etiology. obstruction, abdominal plain films are as sensitive as CT. The American
86
■ WORKUP OF BOWEL OBSTRUCTION AND MANAGEMENT College of Radiology guidelines corroborate this approach, as it lists CT
of the abdomen (with intravenous contrast but not oral contrast) as the
The investigation of intestinal obstruction depends on important clues most appropriate radiologic investigation of a suspected complete or
from the history if available, physical examination, and appropriate high-grade partial small bowel obstruction. CT can provide information
radiologic imaging. A history of clinical obstructive features (vomiting, regarding the presence or absence of obstruction, its anatomical location,
Ileus ± abdominal
distension
X-ray ± No Concerning Yes Consult
bedside U/S abdominal exam? surgery
Medical management &
Ascites
diagnostic ± therapeutic tap
Free air Consult surgery
Bowel distension Colon only
± air fluid levels
Small bowel Small bowel & Rectal exam
only colon
CT ± surgery consult Normal Tumor or Feces
to R/O obstruction stricture
Risk factors or signs of possible volvulus, Consult surgery Disimpaction
bowel ischemia, or tumor?
No Yes
Manage as ileus/ Surgery consult
pseudoobstruction ± CT
Unresolved
FIGURE 104-6. Algorithm for evaluation of ileus ± abdominal distension.
section09.indd 1005 1/14/2015 9:27:07 AM