Page 1463 - Hall et al (2015) Principles of Critical Care-McGraw-Hill
P. 1463
1002 PART 9: Gastrointestinal Disorders
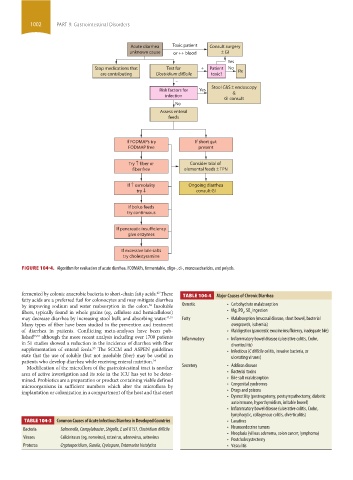
Acute diarrhea Toxic patient Consult surgery
unknown cause or ++ blood ± GI
Yes
Stop medications that Test for + Patient No Rx
are contributing Clostridium difficile toxic?
–
Stool C&S ± endoscopy
Risk factors for Yes &
infection
GI consult
No
Assess enteral
feeds
If FODMAPs try If short gut
FODMAP free present
Try fiber or Consider trial of
fiber free elemental feeds ± TPN
If osmolality Ongoing diarrhea
try consult GI
If bolus feeds
try continuous
If pancreatic insufficiency
give enzymes
If excessive bile salts
try cholestyramine
FIGURE 104-4. Algorithm for evaluation of acute diarrhea. FODMAPs, fermentable, oligo-, di-, monosaccharides, and polyols.
fermented by colonic anaerobic bacteria to short-chain fatty acids. These TABLE 104-4 Major Causes of Chronic Diarrhea
42
fatty acids are a preferred fuel for colonocytes and may mitigate diarrhea
by improving sodium and water reabsorption in the colon. Insoluble Osmotic • Carbohydrate malabsorption
52
fibers, typically found in whole grains (eg, cellulose and hemicellulose) • Mg, PO , SO ingestion
4
4
may decrease diarrhea by increasing stool bulk and absorbing water. 42,51 Fatty • Malabsorption (mucosal disease, short bowel, bacterial
Many types of fiber have been studied in the prevention and treatment overgrowth, ischemia)
of diarrhea in patients. Conflicting meta-analyses have been pub- • Maldigestion (pancreatic exocrine insufficiency, inadequate bile)
lished 53,54 although the more recent analysis including over 1700 patients Inflammatory • Inflammatory bowel disease (ulcerative colitis, Crohn,
in 51 studies showed a reduction in the incidence of diarrhea with fiber diverticulitis)
supplementation of enteral feeds. The SCCM and ASPEN guidelines • Infectious (C difficile colitis, invasive bacteria, or
53
state that the use of soluble (but not insoluble fiber) may be useful in ulcerating viruses)
patients who develop diarrhea while receiving enteral nutrition. 34
Modification of the microflora of the gastrointestinal tract is another Secretory • Addison disease
area of active investigation and its role in the ICU has yet to be deter- • Bacterial toxins
mined. Probiotics are a preparation or product containing viable defined • Bile salt malabsorption
microorganisms in sufficient numbers which alter the microflora by • Congenital syndromes
implantation or colonization in a compartment of the host and that exert • Drugs and poisons
• Dysmotility (postvagotomy, postsympathectomy, diabetic
autoimmune, hyperthyroidism, irritable bowel)
• Inflammatory bowel disease (ulcerative colitis, Crohn,
lymphocytic, collagenous colitis, diverticulitis)
TABLE 104-3 Common Causes of Acute Infectious Diarrhea in Developed Countries • Laxatives
Bacteria Salmonella, Campylobacter, Shigella, E coli 0157, Clostridium difficile • Neuroendocrine tumors
• Neoplasia (villous adenoma, colon cancer, lymphoma)
Viruses Caliciviruses (eg, norovirus), rotavirus, adenovirus, astrovirus • Postcholecystectomy
Protozoa Cryptosporidium, Giardia, Cyclospora, Entamoeba histolytica • Vasculitis
section09.indd 1002 1/14/2015 9:27:06 AM