Page 1468 - Hall et al (2015) Principles of Critical Care-McGraw-Hill
P. 1468
CHAPTER 104: Jaundice, Diarrhea, Obstruction, and Pseudoobstruction 1007
investigation for an underlying obstructive or otherwise sinister etiology the initial therapy of ACPO is supportive and aimed at alleviating any
(eg, such as an intra-abdominal abscess) should be considered. predisposing factors and encouraging spontaneous resolution (see
■ ACUTE COLONIC PSEUDOOBSTRUCTION Fig. 104-7). The major risk factors for complications and poor outcome
are the amount and duration of colonic distension.
By Laplace law,
113,118
In 1948, Sir William Heneage Ogilvie described two cases of colonic tension in the wall of the cecum is proportional to its radius. When the
dilation without obstruction, a phenomenon which was subsequently cecal wall tension exceeds that of capillary perfusion pressure, ischemia
110
called Ogilvie syndrome. In the early 1980s, the term acute colonic pseu- results and this can progress to infarction and perforation. Retrospective
doobstruction (ACPO) was introduced. 111 analysis of over 400 reported cases in the literature has shown that the
ACPO is characterized by massive colonic dilation with symptoms risk of cecal perforation is negligible when its diameter is <12 cm, but
and signs of colonic obstruction without mechanical blockage. Although increases steadily with increasing diameter. 113,116 Although duration of
112
its exact prevalence is unknown, it most often affects those in their distension >6 days has been listed as a risk factor in some reviews, 112,119
sixth decade of life with a slight male predominance (60% males). It examination of the primary literature reveals this number is based on
113
is reported to occur in approximately 1% of orthopedic procedures, a series of only 25 patients, five of which perforated, and of note, all
114
but is almost exclusively restricted to hospitalized or institutionalized patients who had cecal dilation for 4 days or less survived. 118
patients with serious underlying medical and/or surgical conditions. Initial therapy includes giving the patient nothing per mouth, placing
Complications occur in 3% to 15% of patients and mortality rate can be a nasogastric suction catheter to limit swallowed air from contributing
up to 50%. 113,115,116 further to colonic distension, intravenous correction of any fluid or
■ PATHOGENESIS OF OGILVIE SYNDROME ing etiologies such as hypothyroidism and infection, discontinuation of
electrolyte imbalances (Na, K, Ca, PO , Mg), investigation for contribut-
4
The exact mechanism of the development of ACPO has not been deter- any possibly offending medications, and mobilization as much as pos-
sible. Oral laxatives are avoided, particularly lactulose which results in
mined, but the most accepted theory is an imbalance in autonomic further gas production via colonic bacterial fermentation. Placement
112
output to the colon, produced by a variety of factors, leading to excessive of a rectal tube ± tap water enemas may be included. Patients should be
parasympathetic suppression or sympathetic stimulation. 112,116 Most followed with serial physical examinations, plain abdominal radiographs
patients who develop ACPO have multiple predisposing factors that every 12 to 24 hours, and serial laboratory tests including complete
include certain drugs, recent trauma or operation, infections, and meta- blood cell count and electrolytes. The reported success rates for this
bolic disturbances (see Table 104-7). approach varies widely from 20% to 92%. 120
■ CLINICAL PRESENTATION OF ACPO It is important to note that if at any point during treatment the
ACPO is characterized by abdominal distension, pain, nausea ± vomiting, patient’s condition deteriorates, investigation for ischemia and perfora-
tion should be undertaking immediately. Patients who fail to improve
with variable passage of flatus or stools. On examination, the abdomen after 24 to 48 hours of conservative therapy should be considered for
is tympanitic and bowel sounds are typically present. Abdominal disten- pharmacological therapy with neostigmine.
sion usually develops over 3 to 7 days but can occur as rapidly as within Neostigmine is an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor that works by
24 hours. The presence of marked abdominal tenderness, fever, and increasing the amount of acetylcholine at the muscarinic receptors in
113
leukocytosis raises the suspicion of ischemia or perforation, although the bowel (and elsewhere), thereby enhancing colonic motor activity.
these findings are neither specific nor reliably sensitive for such com- The onset of action is within a few minutes and lasts 1 to 2 hours
plications. Radiographically, plain abdominal x-rays show colonic dila-
tion primarily involving the proximal colon. Concomitant dilation of
the small bowel suggests an ileus or distal colonic obstruction with an
incompetent ileocecal valve. A reduction in distal colonic diameter or Colonic pseudoobstruction
“cutoff sign” may be present, the presence of which begs the dilemma of
whether there is an actual mechanical obstruction or not.
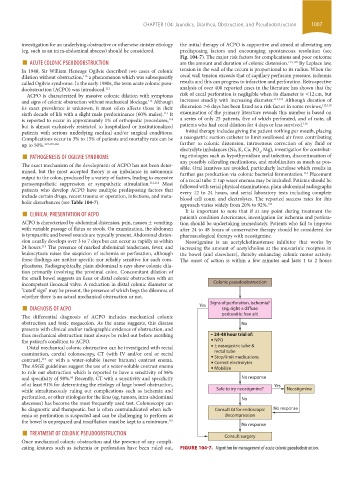
■ DIAGNOSIS OF ACPO Yes Signs of perforation, ischemia?
(eg, right ± diffuse
The differential diagnosis of ACPO includes mechanical colonic peritonitis; free air)
obstruction and toxic megacolon. As the name suggests, this disease No
presents with clinical and/or radiographic evidence of obstruction, and
thus mechanical obstruction must always be ruled out before ascribing ~ 24-48 hour trial of:
the patient’s condition to ACPO. NPO
Distal mechanical colonic obstruction can be investigated with rectal ± nasogastric tube &
examination, careful colonoscopy, CT (with IV and/or oral or rectal rectal tube
contrast), or with a water-soluble (never barium) contrast enema. Stop/limit medications
117
The ASGE guidelines suggest the use of a water-soluble contrast enema Correct electrolytes
Mobilize
to rule out obstruction which is reported to have a sensitivity of 96%
and specificity of 98%. Recently, CT with a sensitivity and specificity No response
89
of at least 91% for determining the etiology of large bowel obstruction, Yes
while simultaneously ruling out complications such as ischemia and Safe to try neostigmine? Neostigmine
perforation, or other etiologies for the ileus (eg, tumors, intra-abdominal No
abscesses) has become the most frequently used test. Colonoscopy can
be diagnostic and therapeutic, but is often contraindicated when isch- Consult GI for endoscopic No response
emia or perforation is suspected and can be challenging to perform as decompression
the bowel is unprepared and insufflation must be kept to a minimum. 116 No response
■ TREATMENT OF COLONIC PSEUDOOBSTRUCTION
Once mechanical colonic obstruction and the presence of any compli- Consult surgery
cating features such as ischemia or perforation have been ruled out, FIGURE 104-7. Algorithm for management of acute colonic pseudoobstruction.
section09.indd 1007 1/14/2015 9:27:08 AM