Page 1620 - Hall et al (2015) Principles of Critical Care-McGraw-Hill
P. 1620
CHAPTER 119: Spinal Injuries 1139
Patient Name
Examiner Name Date/Time of Exam C2
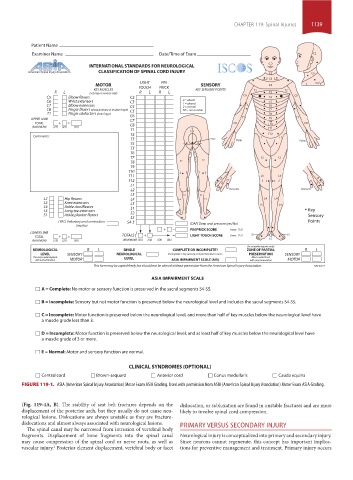
INTERNATIONAL STANDARDS FOR NEUROLOGICAL
American Spinal Injury Association CLASSIFICATION OF SPINAL CORD INJURY C2 C3
C3
MOTOR LIGHT PIN SENSORY C4 C4
KEY MUSCLES TOUCH PRICK KEY SENSORY POINTS T2 T2
R L (scoring on reverse side) R L R L T3
C5 Elbow flexors C2 C5 T4 C5
C6 Wrist extensors C3 0 = absent T5
C7 Elbow extensors C4 1 = altered T6
2 = normal
C8 Finger flexors (distal phalanx of middle finger) C5 NT = not testable T7
T1 Finger abductors (little finger) C6 T8
UPPER LIMB C7 T1 T9 T1
TOTAL + = C6 T10 C6
(MAXIMUM) (25) (25) (50) C8 T11
T1 S 3
T2 T12
Comments:
T3 S4-5 Palm L1 L1 Palm
T4
T5
T6 2 L L 2
T7 L L L2 L2
T8 S2 3 3 S2
T9
T10
T11 L3 L3 C8
T12 C8 C7 C6 C6
L1 C7
L2 L 4 L 4 Dorsum Dorsum
L3 S1 S1
L2 Hip flexors L4 L5 L5 L4 L4
L3 Knee extensors L5 L5 L5
L4 Ankle dorsiflexors S1
L5 Long toe extensors S2 Key
S1 Ankle plantar flexors Sensory
S3
(VAC) Voluntary anal contraction S4-5 (DAP) Deep anal pressure (yes/No) Points
(Yes/No)
+ = PIN PRICK SCORE (max: 112)
LOWER LIMB S1 S1
TOTAL + = TOTALS + = LIGHT TOUCH SCORE (max: 112)
(MAXIMUM) (25) (25) (50) (MAXIMUM) (56) (56) (56) (56) S1
(In complete injuries only)
NEUROLOGICAL R L SINGLE COMPLETE OR INCOMPLETE? ZONE OF PARTIAL R L
LEVEL SENSORY NEUROLOGICAL Incomplete = Any sensory or motor function in s4-s5 PRESERVATION SENSORY
The most caudal segment LEVEL Most caudal level
with normal function MOTOR ASIA IMPAIRMENT SCALE (AIS) with any innervation MOTOR
This form may be copied freely but should not be altered without permission from the American Spinal Injury Association. REV 04/11
ASIA IMPAIRMENT SCALE
A = Complete: No motor or sensory function is preserved in the sacral segments S4-S5.
B = Incomplete: Sensory but not motor function is preserved below the neurological level and includes the sacral segments S4-S5.
C = Incomplete: Motor function is preserved below the neurological level, and more than half of key muscles below the neurological level have
a muscle grade less than 3.
D = Incomplete: Motor function is preserved below the neurological level, and at least half of key muscles below the neurological level have
a muscle grade of 3 or more.
E = Normal: Motor and sensory function are normal.
CLINICAL SYNDROMES (OPTIONAL)
Central cord Brown-sequard Anterior cord Conus medullaris Cauda equina
FIGURE 119-1. ASIA (American Spinal Injury Association) Motor Exam ASIA Grading. Used with permission from ASIA (American Spinal Injury Association) Motor Exam ASIA Grading.
(Fig. 119-4A, B). The stability of seat belt fractures depends on the dislocation, or subluxation are found in unstable fractures and are more
displacement of the posterior arch, but they usually do not cause neu- likely to involve spinal cord compression.
rological lesions. Dislocations are always unstable as they are fracture-
dislocations and almost always associated with neurological lesions. PRIMARY VERSUS SECONDARY INJURY
The spinal canal may be narrowed from intrusion of vertebral body
fragments. Displacement of bone fragments into the spinal canal Neurological injury is conceptualized into primary and secondary injury.
may cause compression of the spinal cord or nerve roots, as well as Since neurons cannot regenerate, this concept has important implica-
vascular injury. Posterior element displacement, vertebral body or facet tions for preventive management and treatment. Primary injury occurs
1
section10.indd 1139 1/20/2015 9:20:25 AM