Page 492 - Clinical Hematology_ Theory _ Procedures ( PDFDrive )
P. 492
476 PART 6 ■ Neoplastic Disorders
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS OF ■ Chil hoo MDS, inclu ing re r ctory cytopeni o chil -
MYELODYSPLASTIC SYNDROME hoo (provision l)
AND MYELODYSPLASTIC/ ■ Myelo yspl stic syn ro e—uncl ssif e (MDS-U)
MYELOPROLIFERATIVE NEOPLASMS ■ I iop thic cytopeni o un eter ine signif c nce (ICUS)
(provision l)
Since the origin l evelop ent o the French-A eric n-
British (FAB) cl ssif c tion or yelo yspl stic syn ro es Etiology
(MDSs) ( ble 24.1), the WHO h s evelope newer cl s-
sif c tion o MDS n yelo yspl stic / yeloproli er tive Pri ry or e novo MDS occurs without known history
neopl s s (MDS/MPNs). T e current WHO public tion o o che other py or r i tion exposure. Secon ry MDS c n
umors and Hematopoietic and Lymphoid issues h s this so eti es be irectly rel te to known gent. Cert in risk
newer cl ssif c tion in 2016 ( ble 24.2). ctors y be possible etiologies or eveloping MDS. T ese
ctors inclu e the ollowing:
■ Age. Popul tion stu ies in Engl n h ve oun th t the
MYELODYSPLASTIC SYNDROMES cru e inci ence incre ses ro 0.5 per 100,000 people
younger th n ge 50 ye rs to 89 per 100,000 people 80
Myelodysplastic syndromes (MDSs) is clon l isor er o the bone
rrow. T e clon l n ture o MDS is supporte by rese rch ye rs o ge or ol er.
stu ies, even in the bsence o etect ble cytogenetic bnor li- ■ Genetic predisposition. F ili l syn ro es h ve been
ties. MDS is ch r cterize by the si ult neous proli er tion n reporte but re r re. F nconi’s ne i , Shw ch n-
poptosis o he topoietic cells th t le to nor l or hyper- Di on syn ro e, n Di on -Bl ck n syn ro e
cellul r bone rrow biopsy n peripher l bloo cytopeni (s). re ssoci te with n incre se risk o MDS.
Leukocytosis is never t n initi l present tion o p tient. ■ Environmental exposures. P rticul rly with benzene n
possibly other in ustri l solvents.
MDS Classi cations ■ Prior therapy. T e gre test inci ence o MDS ollows co -
bine che other py n r i tion ther py. It shoul lso
Seven subtypes o MDS re cl ssif e in the recent WHO be note th t secon ry MDS prece es AML s l te con-
2016 revision. T e subtypes h ve been ren e with so e sequence o che other py or r i tion ther py or both
integr tion o olecul r n lysis. T e MDSs re cl ssif e in ny tre te p tients. For lkyl ting gents, the risk o
into v rious types o re r ctory ne i s (RAs), uncl ssif e eveloping secon ry MDS or AML st rts with the en
syn ro e, chil hoo MDS, n MDS ssoci te with iso- o ther py n pe ks t 4 ye rs, with pl te u t 10 ye rs.
l te el(5q). T e specif c subtypes inclu e For epipo ophyllotoxins, the l tency perio to evelop-
ent o MDS/AML is l ost lw ys less th n 5 ye rs, with
■ Re r ctory cytopeni s with uniline ge yspl si , shorter l tency o tr nsition ro MDS to AML.
grouping RA, re r ctory neutropeni , n re r ctory
thro bocytopeni Ex ples o ise ses th t prece e MDS inclu e ov r-
■ Re r ctory ne i with ring si erobl sts (RARSs) i n c rcino tre te with lkyl ting gents (10% to 15%
■ Re r ctory cytopeni with ultiline ge yspl si (RCMD) o MDS c ses), Ho gkin’s ise se tre te with co bine
■ Re r ctory ne i with excess o bl sts (RAEB-1 n ther py (8% to 10% o MDS c ses), n ultiple yelo
RAEB-2) ( pproxi tely 15% o MDS c ses). One theory to expl in
■ MDS ssoci te with isol te el(5q) the in uction o MDS n perh ps eventu l AML is th t
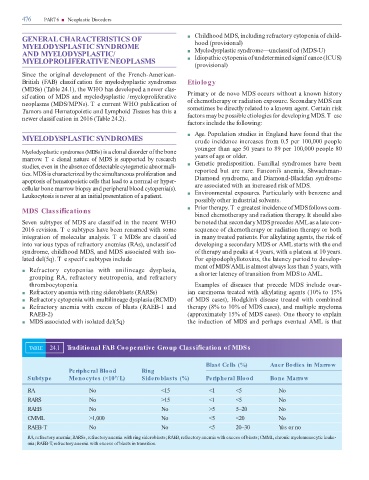
TABLE 24.1 Traditional FAB Cooperative Group Classi cation of MDSs
Blast Cells (%) Auer Bodies in Marrow
Peripheral Blood Ring
Subtype Monocytes (×10 /L) Sideroblasts (%) Peripheral Blood Bone Marrow
9
RA No <15 <1 <5 No
RARS No >15 <1 <5 No
RAEB No No >5 5–20 No
CMML >1,000 No <5 <20 No
RAEB-T No No <5 20–30 Yes or no
RA, refractory anemia; RARSs, refractory anemia with ring sideroblasts; RAEB, refractory anemia with excess of blasts; CMML, chronic myelomonocytic leuke-
mia; RAEB-T, refractory anemia with excess of blasts in transition.