Page 176 - Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology ( PDFDrive )
P. 176
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com CHAPTER 18 Gram-Negative Rods Related to the Enteric Tract 165 mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
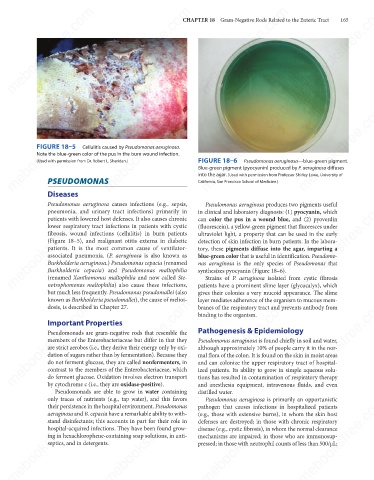
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com FIGURE 18–6 Pseudomonas aeruginosa—blue-green pigment. mebooksfree.com
FIGURE 18–5
Cellulitis caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Note the blue-green color of the pus in the burn wound infection.
(Used with permission from Dr. Robert L. Sheridan.)
Blue-green pigment (pyocyanin) produced by P. aeruginosa diffuses
PSEUDOMONAS
California, San Francisco School of Medicine.)
Diseases into the agar. (Used with permission from Professor Shirley Lowe, University of
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com (fluorescein), a yellow-green pigment that fluoresces under mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
Pseudomonas aeruginosa causes infections (e.g., sepsis,
Pseudomonas aeruginosa produces two pigments useful
pneumonia, and urinary tract infections) primarily in
in clinical and laboratory diagnosis: (1) pyocyanin, which
patients with lowered host defenses. It also causes chronic
can color the pus in a wound blue, and (2) pyoverdin
lower respiratory tract infections in patients with cystic
fibrosis, wound infections (cellulitis) in burn patients
ultraviolet light, a property that can be used in the early
(Figure 18–5), and malignant otitis externa in diabetic
detection of skin infection in burn patients. In the labora-
tory, these pigments diffuse into the agar, imparting a
patients. It is the most common cause of ventilator-
associated pneumonia. (P. aeruginosa is also known as
blue-green color that is useful in identification. Pseudomo-
Burkholderia aeruginosa.) Pseudomonas cepacia (renamed
nas aeruginosa is the only species of Pseudomonas that
Burkholderia cepacia) and Pseudomonas maltophilia
(renamed Xanthomonas maltophilia and now called Ste-
Strains of P. aeruginosa isolated from cystic fibrosis
notrophomonas maltophilia) also cause these infections,
patients have a prominent slime layer (glycocalyx), which
but much less frequently. Pseudomonas pseudomallei (also synthesizes pyocyanin (Figure 18–6).
gives their colonies a very mucoid appearance. The slime
known as Burkholderia pseudomallei), the cause of melioi-
layer mediates adherence of the organism to mucous mem-
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com Pathogenesis & Epidemiology mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
dosis, is described in Chapter 27.
branes of the respiratory tract and prevents antibody from
binding to the organism.
Important Properties
Pseudomonads are gram-negative rods that resemble the
members of the Enterobacteriaceae but differ in that they
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is found chiefly in soil and water,
are strict aerobes (i.e., they derive their energy only by oxi-
although approximately 10% of people carry it in the nor-
dation of sugars rather than by fermentation). Because they
mal flora of the colon. It is found on the skin in moist areas
do not ferment glucose, they are called nonfermenters, in
and can colonize the upper respiratory tract of hospital-
contrast to the members of the Enterobacteriaceae, which
do ferment glucose. Oxidation involves electron transport
tions has resulted in contamination of respiratory therapy
by cytochrome c (i.e., they are oxidase-positive).
and anesthesia equipment, intravenous fluids, and even
Pseudomonads are able to grow in water containing ized patients. Its ability to grow in simple aqueous solu-
distilled water.
only traces of nutrients (e.g., tap water), and this favors
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com defenses are destroyed; in those with chronic respiratory mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is primarily an opportunistic
their persistence in the hospital environment. Pseudomonas
pathogen that causes infections in hospitalized patients
aeruginosa and B. cepacia have a remarkable ability to with-
(e.g., those with extensive burns), in whom the skin host
stand disinfectants; this accounts in part for their role in
hospital-acquired infections. They have been found grow-
disease (e.g., cystic fibrosis), in whom the normal clearance
ing in hexachlorophene-containing soap solutions, in anti-
mechanisms are impaired; in those who are immunosup-
septics, and in detergents.
pressed; in those with neutrophil counts of less than 500/μL;
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com