Page 293 - Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology ( PDFDrive )
P. 293
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
282
PART III Basic Virology
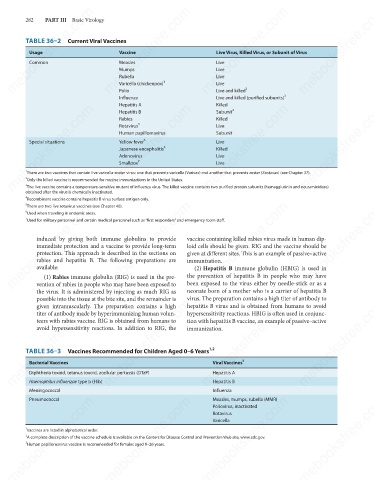
TABLE 36–2 Current Viral Vaccines
Usage
Live Virus, Killed Virus, or Subunit of Virus
Vaccine
Measles
Live
Common
Mumps
Live
Varicella (chickenpox)
Live
Live and killed
Polio
Rubella 1 Live 4 2 3
Live and killed (purified subunits)
Influenza
Hepatitis A
Killed
obtained after the virus is chemically inactivated. mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com Rotavirus 5 7 6 6 mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
Hepatitis B
Subunit
Killed
Rabies
Live
Subunit
Human papillomavirus
Yellow fever
Live
Special situations
Japanese encephalitis
Killed
Adenovirus
Live
Smallpox
Live
1
There are two vaccines that contain live varicella-zoster virus: one that prevents varicella (Varivax) and another that prevents zoster (Zostavax) (see Chapter 37).
The live vaccine contains a temperature-sensitive mutant of influenza virus. The killed vaccine contains two purified protein subunits (hemagglutinin and neuraminidase)
4 2 3 5 6 7 Only the killed vaccine is recommended for routine immunizations in the United States.
Recombinant vaccine contains hepatitis B virus surface antigen only.
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com vaccine containing killed rabies virus made in human dip- mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
There are two live rotavirus vaccines (see Chapter 40).
Used when traveling in endemic areas.
Used for military personnel and certain medical personnel such as “first responders” and emergency room staff.
induced by giving both immune globulins to provide
immediate protection and a vaccine to provide long-term
loid cells should be given. RIG and the vaccine should be
protection. This approach is described in the sections on
given at different sites. This is an example of passive–active
rabies and hepatitis B. The following preparations are
immunization.
available:
(2) Hepatitis B immune globulin (HBIG) is used in
(1) Rabies immune globulin (RIG) is used in the pre-
been exposed to the virus either by needle-stick or as a
vention of rabies in people who may have been exposed to
neonate born of a mother who is a carrier of hepatitis B
the virus. It is administered by injecting as much RIG as the prevention of hepatitis B in people who may have
virus. The preparation contains a high titer of antibody to
possible into the tissue at the bite site, and the remainder is
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com tion with hepatitis B vaccine, an example of passive–active mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
hepatitis B virus and is obtained from humans to avoid
given intramuscularly. The preparation contains a high
titer of antibody made by hyperimmunizing human volun-
hypersensitivity reactions. HBIG is often used in conjunc-
teers with rabies vaccine. RIG is obtained from humans to
avoid hypersensitivity reactions. In addition to RIG, the
immunization.
1,2
TABLE 36–3 Vaccines Recommended for Children Aged 0–6 Years
3
Viral Vaccines
Bacterial Vaccines
Diphtheria toxoid, tetanus toxoid, acellular pertussis (DTaP)
Hepatitis B
Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib)
Meningococcal Hepatitis A
Influenza
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
Measles, mumps, rubella (MMR)
Pneumococcal
Poliovirus, inactivated
Rotavirus
Varicella
1
Vaccines are listed in alphabetical order.
2
A complete description of the vaccine schedule is available on the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Web site, www.cdc.gov.
3
Human papillomavirus vaccine is recommended for females aged 9–26 years.
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com