Page 396 - Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology ( PDFDrive )
P. 396
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
CHAPTER 45 Human Immunodeficiency Virus
385
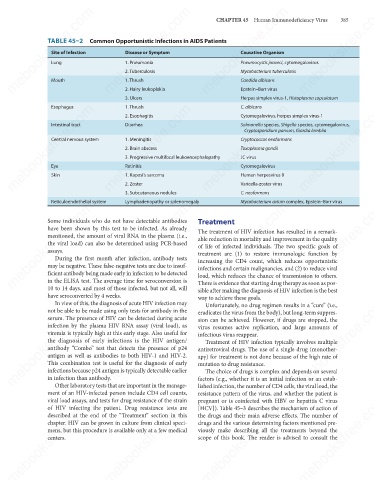
TABLE 45–2 Common Opportunistic Infections in AIDS Patients
Causative Organism
Disease or Symptom
Site of Infection
Lung
1. Pneumonia
Pneumocystis jiroveci, cytomegalovirus
2. Tuberculosis
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Epstein–Barr virus
2. Hairy leukoplakia
Mouth 1. Thrush Candida albicans
Herpes simplex virus-1, Histoplasma capsulatum
3. Ulcers
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
C. albicans
Esophagus
1. Thrush
Cytomegalovirus, herpes simplex virus-1
2. Esophagitis
Intestinal tract
Diarrhea
Salmonella species, Shigella species, cytomegalovirus,
Cryptosporidium parvum, Giardia lamblia
Cryptococcus neoformans
1. Meningitis
Central nervous system
2. Brain abscess
Toxoplasma gondii
3. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy
JC virus
Eye
Cytomegalovirus
Retinitis
Human herpesvirus 8
1. Kaposi’s sarcoma
Skin
2. Zoster
Varicella-zoster virus
3. Subcutaneous nodules
C. neoformans
Lymphadenopathy or splenomegaly
Reticuloendothelial system
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com Treatment Mycobacterium avium complex, Epstein–Barr virus mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
Some individuals who do not have detectable antibodies
have been shown by this test to be infected. As already
The treatment of HIV infection has resulted in a remark-
mentioned, the amount of viral RNA in the plasma (i.e.,
able reduction in mortality and improvement in the quality
the viral load) can also be determined using PCR-based
of life of infected individuals. The two specific goals of
assays.
treatment are (1) to restore immunologic function by
During the first month after infection, antibody tests
increasing the CD4 count, which reduces opportunistic
may be negative. These false-negative tests are due to insuf-
infections and certain malignancies, and (2) to reduce viral
ficient antibody being made early in infection to be detected
in the ELISA test. The average time for seroconversion is
There is evidence that starting drug therapy as soon as pos-
10 to 14 days, and most of those infected, but not all, will
sible after making the diagnosis of HIV infection is the best
have seroconverted by 4 weeks. load, which reduces the chance of transmission to others.
way to achieve these goals.
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com sion can be achieved. However, if drugs are stopped, the mebooksfree.com
In view of this, the diagnosis of acute HIV infection may
Unfortunately, no drug regimen results in a “cure” (i.e.,
not be able to be made using only tests for antibody in the
eradicates the virus from the body), but long-term suppres-
serum. The presence of HIV can be detected during acute
infection by the plasma HIV RNA assay (viral load), as
virus resumes active replication, and large amounts of
viremia is typically high at this early stage. Also useful for
infectious virus reappear.
the diagnosis of early infections is the HIV antigen/
Treatment of HIV infection typically involves multiple
antibody “Combo” test that detects the presence of p24
antiretroviral drugs. The use of a single drug (monother-
antigen as well as antibodies to both HIV-1 and HIV-2.
apy) for treatment is not done because of the high rate of
This combination test is useful for the diagnosis of early
mutation to drug resistance.
infections because p24 antigen is typically detectable earlier
The choice of drugs is complex and depends on several
in infection than antibody.
Other laboratory tests that are important in the manage-
lished infection, the number of CD4 cells, the viral load, the
ment of an HIV-infected person include CD4 cell counts, factors (e.g., whether it is an initial infection or an estab-
resistance pattern of the virus, and whether the patient is
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com drugs and the various determining factors mentioned pre- mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
viral load assays, and tests for drug resistance of the strain
pregnant or is coinfected with HBV or hepatitis C virus
of HIV infecting the patient. Drug resistance tests are
[HCV]). Table 45–3 describes the mechanism of action of
the drugs and their main adverse effects. The number of
described at the end of the “Treatment” section in this
chapter. HIV can be grown in culture from clinical speci-
mens, but this procedure is available only at a few medical
viously make describing all the treatments beyond the
scope of this book. The reader is advised to consult the
centers.
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com