Page 394 - Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology ( PDFDrive )
P. 394
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com gp120, and gp41, are produced, but they neutralize the 383 mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
CHAPTER 45 Human Immunodeficiency Virus
Antibodies against various HIV proteins, such as p24,
integration of viral DNA into the DNA of infected cells.
Although the use of powerful antiviral drugs (see “Treat-
virus poorly in vivo and appear to have little effect on the
ment” section later) can significantly reduce the amount
of HIV being produced, the silent, latent infection in
course of the disease.
CD4-positive memory T cells can be activated and serve
HIV has three main mechanisms by which it evades the
as a continuing source of virus.
DNA, resulting in a persistent infection; (2) a high rate of
Elite controllers are a rare group of HIV-infected peo-
ple (less than 1% of those infected) who have no detectable
mutation of the env gene; and (3) the production of the Tat
and Nef proteins that downregulate class I MHC proteins
HIV in their blood. Their CD4 counts are normal without immune system: (1) integration of viral DNA into host cell
mebooksfree.com
using antiretroviral drugs. The ability to be an elite control-
required for cytotoxic T cells to recognize and kill HIV-
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com destruction by the immune system. mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
ler does not depend on gender, race, or mode of acquisition
infected cells. The ability of HIV to infect and kill CD4-
positive helper T cells further enhances its capacity to avoid
of the virus. Although the mechanism is unclear, there is
evidence that certain HLA alleles are protective and that an
inhibitor of the cyclin-dependent kinase known as p21
Clinical Findings
plays an important role.
In addition, there is a group of HIV-infected individuals
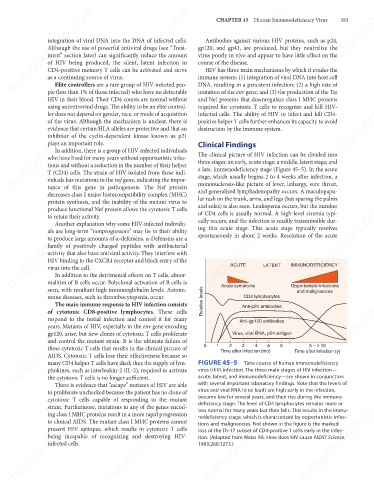
The clinical picture of HIV infection can be divided into
who have lived for many years without opportunistic infec-
three stages: an early, acute stage; a middle, latent stage; and
tions and without a reduction in the number of their helper
a late, immunodeficiency stage (Figure 45–5). In the acute
T (CD4) cells. The strain of HIV isolated from these indi-
viduals has mutations in the nef gene, indicating the impor-
mononucleosis-like picture of fever, lethargy, sore throat,
tance of this gene in pathogenesis. The Nef protein
and generalized lymphadenopathy occurs. A maculopapu-
decreases class I major histocompatibility complex (MHC) stage, which usually begins 2 to 4 weeks after infection, a
lar rash on the trunk, arms, and legs (but sparing the palms
protein synthesis, and the inability of the mutant virus to
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com cally occurs, and the infection is readily transmissible dur- mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
and soles) is also seen. Leukopenia occurs, but the number
produce functional Nef protein allows the cytotoxic T cells
of CD4 cells is usually normal. A high-level viremia typi-
to retain their activity.
Another explanation why some HIV-infected individu-
ing this acute stage. This acute stage typically resolves
als are long-term “nonprogressors” may lie in their ability
spontaneously in about 2 weeks. Resolution of the acute
to produce large amounts of α-defensins. α-Defensins are a
family of positively charged peptides with antibacterial
activity that also have antiviral activity. They interfere with
HIV binding to the CXCR4 receptor and block entry of the
IMMUNODEFICIENCY
LATENT
ACUTE
virus into the cell.
In addition to the detrimental effects on T cells, abnor-
malities of B cells occur. Polyclonal activation of B cells is
seen, with resultant high immunoglobulin levels. Autoim-
and malignancies
mune diseases, such as thrombocytopenia, occur. Relative levels Acute symptoms Opportunistic infections
CD4 lymphocytes
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com FIGURE 45–5 Anti-gp120 antibodies Time after infection (y) mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
The main immune response to HIV infection consists
Anti-p24 antibodies
of cytotoxic CD8-positive lymphocytes. These cells
respond to the initial infection and control it for many
years. Mutants of HIV, especially in the env gene encoding
gp120, arise, but new clones of cytotoxic T cells proliferate
Virus, viral RNA, p24 antigen
and control the mutant strain. It is the ultimate failure of
6
2
3
1
5
4
0
3 – ≥ 10
these cytotoxic T cells that results in the clinical picture of
Time after infection (mo)
AIDS. Cytotoxic T cells lose their effectiveness because so
many CD4 helper T cells have died; thus the supply of lym-
Time course of human immunodeficiency
phokines, such as interleukin-2 (IL-2), required to activate
acute, latent, and immunodeficiency—are shown in conjunction
the cytotoxic T cells is no longer sufficient.
with several important laboratory findings. Note that the levels of
There is evidence that “escape” mutants of HIV are able
virus and viral RNA (viral load) are high early in the infection,
to proliferate unchecked because the patient has no clone of virus (HIV) infection. The three main stages of HIV infection—
become low for several years, and then rise during the immuno-
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com nodeficiency stage, which is characterized by opportunistic infec- mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
cytotoxic T cells capable of responding to the mutant
deficiency stage. The level of CD4 lymphocytes remains more or
strain. Furthermore, mutations in any of the genes encod-
less normal for many years but then falls. This results in the immu-
ing class I MHC proteins result in a more rapid progression
to clinical AIDS. The mutant class I MHC proteins cannot
tions and malignancies. Not shown in the figure is the marked
present HIV epitopes, which results in cytotoxic T cells
loss of the Th-17 subset of CD4-positive T cells early in the infec-
being incapable of recognizing and destroying HIV-
tion. (Adapted from Weiss RA. How does HIV cause AIDS? Science.
infected cells.
1993;260:1273.)
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com