Page 391 - Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology ( PDFDrive )
P. 391
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
PART IV Clinical Virology
380
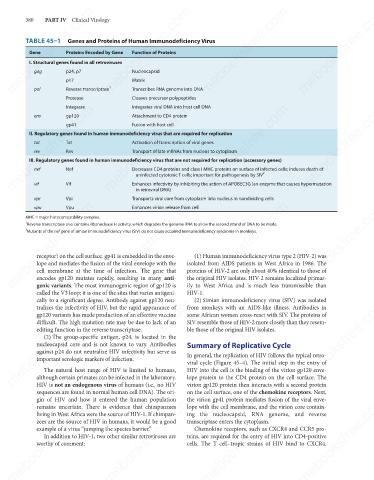
TABLE 45–1 Genes and Proteins of Human Immunodeficiency Virus
Function of Proteins
Gene
Proteins Encoded by Gene
I. Structural genes found in all retroviruses
gag
Nucleocapsid
p24, p7
Reverse transcriptase
Transcribes RNA genome into DNA
Cleaves precursor polypeptides
Protease
pol p17 1 Matrix
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
Integrates viral DNA into host cell DNA
Integrase
Attachment to CD4 protein
env
gp120
gp41
Fusion with host cell
II. Regulatory genes found in human immunodeficiency virus that are required for replication
Tat
tat
Activation of transcription of viral genes
rev
Transport of late mRNAs from nucleus to cytoplasm
Rev
III. Regulatory genes found in human immunodeficiency virus that are not required for replication (accessory genes)
Nef
Decreases CD4 proteins and class I MHC proteins on surface of infected cells; induces death of
nef
2
uninfected cytotoxic T cells; important for pathogenesis by SIV
vif
in retroviral DNA)
Transports viral core from cytoplasm into nucleus in nondividing cells
Vpr
vpr Vif Enhances infectivity by inhibiting the action of APOBEC3G (an enzyme that causes hypermutation
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com isolated from AIDS patients in West Africa in 1986. The mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
Enhances virion release from cell
Vpu
vpu
MHC = major histocompatibility complex.
1
Reverse transcriptase also contains ribonuclease H activity, which degrades the genome RNA to allow the second strand of DNA to be made.
2
Mutants of the nef gene of simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) do not cause acquired immunodeficiency syndrome in monkeys.
receptor) on the cell surface. gp41 is embedded in the enve-
(1) Human immunodeficiency virus type 2 (HIV-2) was
lope and mediates the fusion of the viral envelope with the
cell membrane at the time of infection. The gene that
the original HIV isolates. HIV-2 remains localized primar-
encodes gp120 mutates rapidly, resulting in many anti-
ily to West Africa and is much less transmissible than
genic variants. The most immunogenic region of gp120 is
called the V3 loop; it is one of the sites that varies antigeni- proteins of HIV-2 are only about 40% identical to those of
HIV-1.
(2) Simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) was isolated
cally to a significant degree. Antibody against gp120 neu-
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com SIV resemble those of HIV-2 more closely than they resem- mebooksfree.com
from monkeys with an AIDS-like illness. Antibodies in
tralizes the infectivity of HIV, but the rapid appearance of
some African women cross-react with SIV. The proteins of
gp120 variants has made production of an effective vaccine
difficult. The high mutation rate may be due to lack of an
ble those of the original HIV isolates.
editing function in the reverse transcriptase.
(2) The group-specific antigen, p24, is located in the
Summary of Replicative Cycle
nucleocapsid core and is not known to vary. Antibodies
against p24 do not neutralize HIV infectivity but serve as
In general, the replication of HIV follows the typical retro-
important serologic markers of infection.
viral cycle (Figure 45–4). The initial step in the entry of
The natural host range of HIV is limited to humans,
lope protein to the CD4 protein on the cell surface. The
although certain primates can be infected in the laboratory.
virion gp120 protein then interacts with a second protein
HIV is not an endogenous virus of humans (i.e., no HIV
sequences are found in normal human cell DNA). The ori- HIV into the cell is the binding of the virion gp120 enve-
on the cell surface, one of the chemokine receptors. Next,
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com transcriptase enters the cytoplasm. mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
gin of HIV and how it entered the human population
the virion gp41 protein mediates fusion of the viral enve-
lope with the cell membrane, and the virion core contain-
remains uncertain. There is evidence that chimpanzees
ing the nucleocapsid, RNA genome, and reverse
living in West Africa were the source of HIV-1. If chimpan-
zees are the source of HIV in humans, it would be a good
Chemokine receptors, such as CXCR4 and CCR5 pro-
example of a virus “jumping the species barrier.”
teins, are required for the entry of HIV into CD4-positive
In addition to HIV-1, two other similar retroviruses are
cells. The T cell–tropic strains of HIV bind to CXCR4,
worthy of comment:
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com