Page 445 - Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology ( PDFDrive )
P. 445
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
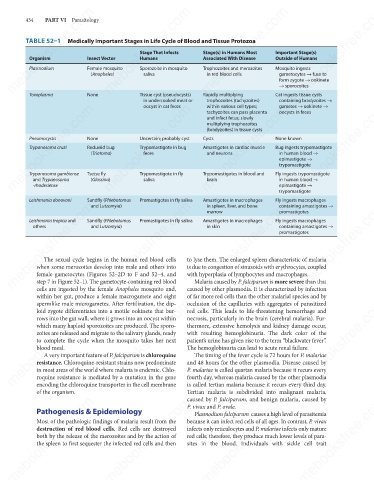
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com Insect Vector Stage That Infects Stage(s) in Humans Most Important Stage(s) mebooksfree.com
PART VI Parasitology
434
TABLE 52–1 Medically Important Stages in Life Cycle of Blood and Tissue Protozoa
Associated With Disease
Humans
Outside of Humans
Organism
Plasmodium
Trophozoites and merozoites
Female mosquito
Sporozoite in mosquito
Mosquito ingests
in red blood cells
gametocytes → fuse to
saliva
(Anopheles)
form zygote → ookinete
→ sporozoites
Tissue cyst (pseudocysts)
None
Toxoplasma
containing bradyzoites →
in undercooked meat or Rapidly multiplying Cat ingests tissue cysts
trophozoites (tachyzoites)
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com None mebooksfree.com Cysts None known mebooksfree.com
trypomastigote mebooksfree.com
oocyst in cat feces
within various cell types;
gametes → ookinete →
oocysts in feces
tachyzoites can pass placenta
and infect fetus; slowly
multiplying trophozoites
(bradyzoites) in tissue cysts
Pneumocystis
Uncertain; probably cyst
Bug ingests trypomastigote
Trypomastigote in bug
Trypanosoma cruzi
Amastigotes in cardiac muscle
Reduviid bug
and neurons
feces
(Triatoma)
in human blood →
epimastigote →
trypomastigote
Trypomastigote in fly
Trypomastigotes in blood and
Trypanosoma gambiense
Fly ingests trypomastigote
Tsetse fly
saliva
in human blood →
brain
(Glossina)
and Trypanosoma
-rhodesiense
epimastigote →
Leishmania donovani Sandfly (Phlebotomus Promastigotes in fly saliva Amastigotes in macrophages Fly ingests macrophages
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com and Lutzomyia) to lyse them. The enlarged spleen characteristic of malaria mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
and Lutzomyia)
in spleen, liver, and bone
containing amastigotes →
marrow
promastigotes
Fly ingests macrophages
Leishmania tropica and
Amastigotes in macrophages
Promastigotes in fly saliva
Sandfly (Phlebotomus
containing amastigotes →
others
in skin
promastigotes
The sexual cycle begins in the human red blood cells
is due to congestion of sinusoids with erythrocytes, coupled
when some merozoites develop into male and others into
female gametocytes (Figures 52–2D to F and 52–4, and
step 7 in Figure 52–1). The gametocyte-containing red blood
Malaria caused by P. falciparum is more severe than that
caused by other plasmodia. It is characterized by infection
cells are ingested by the female Anopheles mosquito and,
of far more red cells than the other malarial species and by
within her gut, produce a female macrogamete and eight with hyperplasia of lymphocytes and macrophages.
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com thermore, extensive hemolysis and kidney damage occur, mebooksfree.com
occlusion of the capillaries with aggregates of parasitized
spermlike male microgametes. After fertilization, the dip-
red cells. This leads to life-threatening hemorrhage and
loid zygote differentiates into a motile ookinete that bur-
rows into the gut wall, where it grows into an oocyst within
necrosis, particularly in the brain (cerebral malaria). Fur-
which many haploid sporozoites are produced. The sporo-
with resulting hemoglobinuria. The dark color of the
zoites are released and migrate to the salivary glands, ready
patient’s urine has given rise to the term “blackwater fever”.
to complete the cycle when the mosquito takes her next
The hemoglobinuria can lead to acute renal failure.
blood meal.
A very important feature of P. falciparum is chloroquine
The timing of the fever cycle is 72 hours for P. malariae
resistance. Chloroquine-resistant strains now predominate
and 48 hours for the other plasmodia. Disease caused by
in most areas of the world where malaria is endemic. Chlo-
fourth day, whereas malaria caused by the other plasmodia
roquine resistance is mediated by a mutation in the gene
is called tertian malaria because it recurs every third day.
encoding the chloroquine transporter in the cell membrane
Tertian malaria is subdivided into malignant malaria,
of the organism. P. malariae is called quartan malaria because it recurs every
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com because it can infect red cells of all ages. In contrast, P. vivax mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
caused by P. falciparum, and benign malaria, caused by
P. vivax and P. ovale.
Pathogenesis & Epidemiology
Plasmodium falciparum causes a high level of parasitemia
Most of the pathologic findings of malaria result from the
infects only reticulocytes and P. malariae infects only mature
destruction of red blood cells. Red cells are destroyed
red cells; therefore, they produce much lower levels of para-
both by the release of the merozoites and by the action of
sites in the blood. Individuals with sickle cell trait
the spleen to first sequester the infected red cells and then
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com