Page 530 - Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology ( PDFDrive )
P. 530
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com Chemistry Attracts CHAPTER 58 Cellular Basis of the Immune Response 519 mebooksfree.com
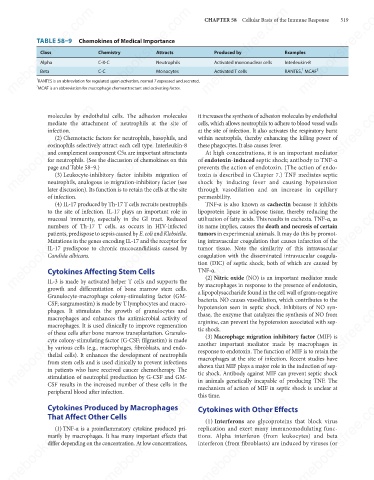
TABLE 58–9 Chemokines of Medical Importance
Class
Examples
Produced by
C-X-C
Neutrophils
Interleukin-8
Activated mononuclear cells
Alpha
2
1
RANTES, MCAF
Monocytes
Beta
Activated T cells
C-C
1
RANTES is an abbreviation for regulated upon activation, normal T expressed and secreted.
2
MCAF is an abbreviation for macrophage chemoattractant and activating factor.
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com it increases the synthesis of adhesion molecules by endothelial mebooksfree.com
molecules by endothelial cells. The adhesion molecules
cells, which allows neutrophils to adhere to blood vessel walls
mediate the attachment of neutrophils at the site of
at the site of infection. It also activates the respiratory burst
infection.
(2) Chemotactic factors for neutrophils, basophils, and
within neutrophils, thereby enhancing the killing power of
eosinophils selectively attract each cell type. Interleukin-8
these phagocytes. It also causes fever.
and complement component C5a are important attractants
At high concentrations, it is an important mediator
of endotoxin-induced septic shock; antibody to TNF-α
for neutrophils. (See the discussion of chemokines on this
prevents the action of endotoxin. (The action of endo-
page and Table 58–9.)
(3) Leukocyte-inhibitory factor inhibits migration of
neutrophils, analogous to migration-inhibitory factor (see
shock by inducing fever and causing hypotension
later discussion). Its function is to retain the cells at the site
through vasodilation and an increase in capillary
permeability.
of infection. toxin is described in Chapter 7.) TNF mediates septic
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com its name implies, causes the death and necrosis of certain mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
TNF-α is also known as cachectin because it inhibits
mebooksfree.com
(4) IL-17 produced by Th-17 T cells recruits neutrophils
lipoprotein lipase in adipose tissue, thereby reducing the
to the site of infection. IL-17 plays an important role in
utilization of fatty acids. This results in cachexia. TNF-α, as
mucosal immunity, especially in the GI tract. Reduced
numbers of Th-17 T cells, as occurs in HIV-infected
tumors in experimental animals. It may do this by promot-
patients, predispose to sepsis caused by E. coli and Klebsiella.
ing intravascular coagulation that causes infarction of the
Mutations in the genes encoding IL-17 and the receptor for
IL-17 predispose to chronic mucocandidiasis caused by
tumor tissue. Note the similarity of this intravascular
coagulation with the disseminated intravascular coagula-
Candida albicans.
tion (DIC) of septic shock, both of which are caused by
Cytokines Affecting Stem Cells
TNF-α.
(2) Nitric oxide (NO) is an important mediator made
IL-3 is made by activated helper T cells and supports the
growth and differentiation of bone marrow stem cells.
a lipopolysaccharide found in the cell wall of gram-negative
Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM- by macrophages in response to the presence of endotoxin,
bacteria. NO causes vasodilation, which contributes to the
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com arginine, can prevent the hypotension associated with sep- mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
CSF; sargramostim) is made by T lymphocytes and macro-
hypotension seen in septic shock. Inhibitors of NO syn-
phages. It stimulates the growth of granulocytes and
thase, the enzyme that catalyzes the synthesis of NO from
macrophages and enhances the antimicrobial activity of
macrophages. It is used clinically to improve regeneration
tic shock.
of these cells after bone marrow transplantation. Granulo-
(3) Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) is
cyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF; filgrastim) is made
another important mediator made by macrophages in
by various cells (e.g., macrophages, fibroblasts, and endo-
response to endotoxin. The function of MIF is to retain the
thelial cells). It enhances the development of neutrophils
macrophages at the site of infection. Recent studies have
from stem cells and is used clinically to prevent infections
shown that MIF plays a major role in the induction of sep-
in patients who have received cancer chemotherapy. The
stimulation of neutrophil production by G-CSF and GM-
in animals genetically incapable of producing TNF. The
CSF results in the increased number of these cells in the
mechanism of action of MIF in septic shock is unclear at
peripheral blood after infection. tic shock. Antibody against MIF can prevent septic shock
this time.
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com replication and exert many immunomodulating func- mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
Cytokines Produced by Macrophages
Cytokines with Other Effects
That Affect Other Cells
(1) Interferons are glycoproteins that block virus
(1) TNF-α is a proinflammatory cytokine produced pri-
tions. Alpha interferon (from leukocytes) and beta
marily by macrophages. It has many important effects that
differ depending on the concentration. At low concentrations,
interferon (from fibroblasts) are induced by viruses (or
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com