Page 534 - Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology ( PDFDrive )
P. 534
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com 1 1 mebooksfree.com lgD mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
523
CHAPTER 59 Antibodies
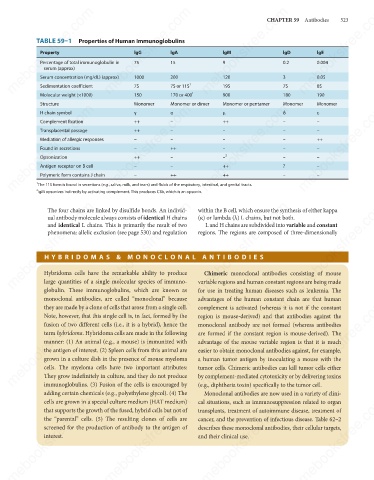
TABLE 59–1 Properties of Human Immunoglobulins
lgM
Property
lgA
lgE
lgG
15
0.004
Percentage of total immunoglobulin in
75
0.2
9
serum (approx)
3
120
200
Serum concentration (mg/dL) (approx)
1000
0.05
7S
19S
7S
7S or 11S
Sedimentation coefficient
8S
900
170 or 400
150
180
190
Molecular weight (×1000)
Monomer or dimer
Structure
Monomer
Monomer
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com Monomer or pentamer Monomer mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
IgM opsonizes indirectly by activating complement. This produces C3b, which is an opsonin. mebooksfree.com
H chain symbol
γ
ε
δ
μ
α
–
++
++
Complement fixation
–
–
–
–
–
–
++
Transplacental passage
–
Mediation of allergic responses
–
++
–
–
–
–
++
–
–
Found in secretions
2
–
Opsonization
++
–
–
–
?
++
–
–
–
Antigen receptor on B cell
–
++
–
–
++
Polymeric form contains J chain
1
The 11S form is found in secretions (e.g., saliva, milk, and tears) and fluids of the respiratory, intestinal, and genital tracts.
2
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com within the B cell, which ensure the synthesis of either kappa mebooksfree.com
The four chains are linked by disulfide bonds. An individ-
(κ) or lambda (λ) L chains, but not both.
ual antibody molecule always consists of identical H chains
and identical L chains. This is primarily the result of two
L and H chains are subdivided into variable and constant
phenomena: allelic exclusion (see page 530) and regulation
regions. The regions are composed of three-dimensionally
H Y BRIDOM AS & MONOCL ONAL ANTIBODIES
Hybridoma cells have the remarkable ability to produce
Chimeric monoclonal antibodies consisting of mouse
large quantities of a single molecular species of immuno-
variable regions and human constant regions are being made
globulin. These immunoglobulins, which are known as
for use in treating human diseases such as leukemia. The
monoclonal antibodies, are called “monoclonal” because
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com advantages of the human constant chain are that human mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
they are made by a clone of cells that arose from a single cell.
complement is activated (whereas it is not if the constant
region is mouse-derived) and that antibodies against the
Note, however, that this single cell is, in fact, formed by the
monoclonal antibody are not formed (whereas antibodies
fusion of two different cells (i.e., it is a hybrid), hence the
are formed if the constant region is mouse-derived). The
term hybridoma. Hybridoma cells are made in the following
manner: (1) An animal (e.g., a mouse) is immunized with
advantage of the mouse variable region is that it is much
the antigen of interest. (2) Spleen cells from this animal are
easier to obtain monoclonal antibodies against, for example,
a human tumor antigen by inoculating a mouse with the
grown in a culture dish in the presence of mouse myeloma
tumor cells. Chimeric antibodies can kill tumor cells either
cells. The myeloma cells have two important attributes:
They grow indefinitely in culture, and they do not produce
immunoglobulins. (3) Fusion of the cells is encouraged by
(e.g., diphtheria toxin) specifically to the tumor cell.
Monoclonal antibodies are now used in a variety of clini-
adding certain chemicals (e.g., polyethylene glycol). (4) The by complement-mediated cytotoxicity or by delivering toxins
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com cancer, and the prevention of infectious disease. Table 62–2 mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
cal situations, such as immunosuppression related to organ
cells are grown in a special culture medium (HAT medium)
transplants, treatment of autoimmune disease, treatment of
that supports the growth of the fused, hybrid cells but not of
the “parental” cells. (5) The resulting clones of cells are
screened for the production of antibody to the antigen of
describes these monoclonal antibodies, their cellular targets,
and their clinical use.
interest.
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com