Page 535 - Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology ( PDFDrive )
P. 535
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com Spleen cells Mix these two populations Myeloma cells mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
PART VII Immunology
524
that do not make
from animal
immunized
any immunoglobulins
against antigen
of interest
of cells and add fusing agent
Fused cells (hybridoma cells)
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com Single hybridoma cell is placed mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
are selected in special medium
and unfused cells die
in a well and monitored for production
of monoclonal antibody against antigen
of interest
FIGURE 59–1
Production of monoclonal antibodies.
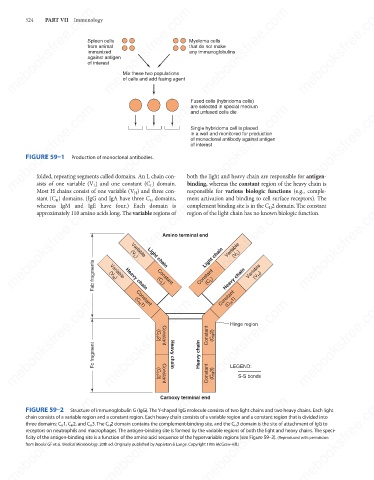
folded, repeating segments called domains. An L chain con-
binding, whereas the constant region of the heavy chain is
sists of one variable (V ) and one constant (C ) domain.
L
L
Most H chains consist of one variable (V ) and three con-
responsible for various biologic functions (e.g., comple-
H
ment activation and binding to cell surface receptors). The
stant (C ) domains. (IgG and IgA have three C domains, both the light and heavy chain are responsible for antigen-
H
H
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com s t n e m g a r f b a F mebooksfree.com Constant (C L ) Heavy chain Variable (V H ) mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
complement binding site is in the C 2 domain. The constant
whereas IgM and IgE have four.) Each domain is
H
region of the light chain has no known biologic function.
approximately 110 amino acids long. The variable regions of
Amino terminal end
Variable
Light chain
(V L )
Variable
(V L )
Light chain
Variable
(V H )
Constant
(C L )
Heavy chain
Constant
(C H 1)
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com t n e m g a r f c F mebooksfree.com Heavy chain mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
Constant
(C H 1)
Hinge region
Constant
(C H 2)
(C H 2)
Constant
LEGEND:
Constant
(C H 3)
Heavy chain
S-S bonds
(C H 3)
Constant
Carboxy terminal end
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
FIGURE 59–2
Structure of immunoglobulin G (IgG). The Y-shaped IgG molecule consists of two light chains and two heavy chains. Each light
chain consists of a variable region and a constant region. Each heavy chain consists of a variable region and a constant region that is divided into
three domains: C H 1, C H 2, and C H 3. The C H 2 domain contains the complement-binding site, and the C H 3 domain is the site of attachment of IgG to
receptors on neutrophils and macrophages. The antigen-binding site is formed by the variable regions of both the light and heavy chains. The speci-
ficity of the antigen-binding site is a function of the amino acid sequence of the hypervariable regions (see Figure 59–3). (Reproduced with permission
from Brooks GF et al. Medical Microbiology. 20th ed. Originally published by Appleton & Lange. Copyright 1995 McGraw-Hill.)
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com