Page 539 - Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology ( PDFDrive )
P. 539
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com ab c x mebooksfree.com C mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
PART VII Immunology
528
Embryonic/germ line
Heavy-chain gene
IVS
1 23 456
V Hn
V H1
V H2
D H
J H
DNA
rearrangement
Rearranged heavy-chain gene DNA V H2 b2 3 45 6 IVS C
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com Transcription mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
J
D
RNA splicing
IgM mRNA
C
V H DJ
Translation
IgM protein
V H DJ C
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com chain [κL], lambda light chain [λL], and the five heavy mebooksfree.com
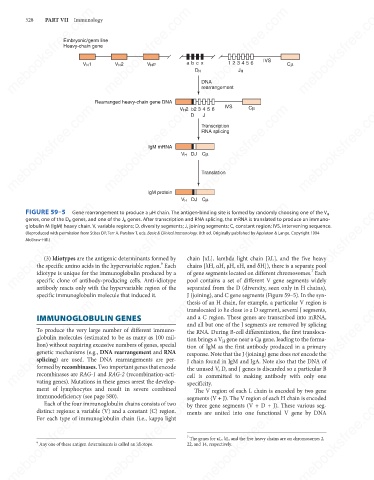
FIGURE 59–5
Gene rearrangement to produce a μH chain. The antigen-binding site is formed by randomly choosing one of the V H
genes, one of the D H genes, and one of the J H genes. After transcription and RNA splicing, the mRNA is translated to produce an immuno-
globulin M (IgM) heavy chain. V, variable regions; D, diversity segments; J, joining segments; C, constant region; IVS, intervening sequence.
(Reproduced with permission from Stites DP, Terr A, Parslow T, eds. Basic & Clinical Immunology. 8th ed. Originally published by Appleton & Lange. Copyright 1994
McGraw-Hill.)
(3) Idiotypes are the antigenic determinants formed by
6
chains [λH, αH, μH, εH, and δH]), there is a separate pool
the specific amino acids in the hypervariable region. Each
7
idiotype is unique for the immunoglobulin produced by a
specific clone of antibody-producing cells. Anti-idiotype
pool contains a set of different V gene segments widely
separated from the D (diversity, seen only in H chains),
antibody reacts only with the hypervariable region of the
J (joining), and C gene segments (Figure 59–5). In the syn-
specific immunoglobulin molecule that induced it. of gene segments located on different chromosomes. Each
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com and all but one of the J segments are removed by splicing mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
thesis of an H chain, for example, a particular V region is
translocated to lie close to a D segment, several J segments,
IMMUNOGLOBULIN GENES
and a C region. These genes are transcribed into mRNA,
To produce the very large number of different immuno-
the RNA. During B-cell differentiation, the first transloca-
globulin molecules (estimated to be as many as 100 mil-
tion brings a V gene near a Cμ gene, leading to the forma-
H
lion) without requiring excessive numbers of genes, special
tion of IgM as the first antibody produced in a primary
genetic mechanisms (e.g., DNA rearrangement and RNA
response. Note that the J (joining) gene does not encode the
splicing) are used. The DNA rearrangements are per-
J chain found in IgM and IgA. Note also that the DNA of
formed by recombinases. Two important genes that encode
recombinases are RAG-1 and RAG-2 (recombination-acti-
cell is committed to making antibody with only one
vating genes). Mutations in these genes arrest the develop-
specificity.
ment of lymphocytes and result in severe combined the unused V, D, and J genes is discarded so a particular B
The V region of each L chain is encoded by two gene
immunodeficiency (see page 580).
segments (V + J). The V region of each H chain is encoded
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com 7 22, and 14, respectively. mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
Each of the four immunoglobulin chains consists of two
by three gene segments (V + D + J). These various seg-
distinct regions: a variable (V) and a constant (C) region.
ments are united into one functional V gene by DNA
For each type of immunoglobulin chain (i.e., kappa light
The genes for κL, λL, and the five heavy chains are on chromosomes 2,
6
Any one of these antigen determinants is called an idiotope.
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com