Page 536 - Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology ( PDFDrive )
P. 536
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com TABLE 59–2 Important Functions of mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
CHAPTER 59 Antibodies
525
Light-chain
hypervariable
Immunoglobulins
regions
Major Functions
Immunoglobulin
Main antibody in the secondary response.
IgG
Opsonizes bacteria, making them easier to
V L
Interchain
phagocytize. Fixes complement, which
V H
disulfide
enhances bacterial killing. Neutralizes
bonds
bacterial toxins and viruses. Crosses the
C L
C L
placenta.
C H1 hypervariable IgA Secretory IgA prevents attachment of bacteria
C H1
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com C H2 mebooksfree.com IgM Produced in the primary response to an mebooksfree.com
and viruses to mucous membranes. Does not
Heavy-chain
fix complement.
regions
C H2
antigen. Fixes complement. Does not cross
the placenta. Antigen receptor on the surface
of B cells.
IgD
Uncertain. Found on the surface of many B cells
C H3
as well as in serum.
C H3
Mediates immediate hypersensitivity by
IgE
causing release of mediators from mast cells
A
and basophils upon exposure to antigen
(allergen). Defends against worm infections by
Antigen-binding site
causing release of enzymes from eosinophils.
Does not fix complement. Main host defense
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com pates in the antigen-binding site. H chains are distinct for mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
against helminth infections.
Hypervariable
Hypervariable
regions of
regions of
heavy chain
light chain
The amino-terminal portion of each L chain partici-
B
each of the five immunoglobulin classes and are desig-
nated γ, α, μ, ε, and δ (Table 59–2). The amino-terminal
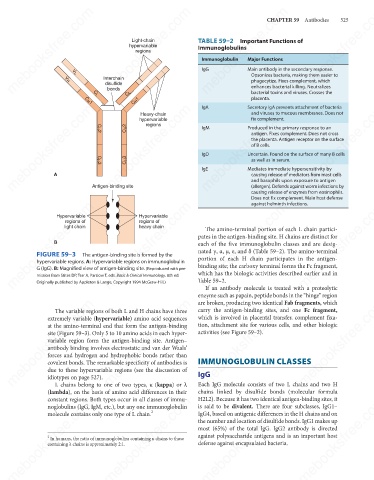
FIGURE 59–3
The antigen-binding site is formed by the
portion of each H chain participates in the antigen-
hypervariable regions. A: Hypervariable regions on immunoglobulin
binding site; the carboxy terminal forms the Fc fragment,
G (IgG). B: Magnified view of antigen-binding site. (Reproduced with per-
which has the biologic activities described earlier and in
mission from Stites DP, Terr A, Parslow T, eds. Basic & Clinical Immunology. 8th ed.
Table 59–2.
Originally published by Appleton & Lange. Copyright 1994 McGraw-Hill.)
If an antibody molecule is treated with a proteolytic
enzyme such as papain, peptide bonds in the “hinge” region
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com tion, attachment site for various cells, and other biologic mebooksfree.com
are broken, producing two identical Fab fragments, which
carry the antigen-binding sites, and one Fc fragment,
The variable regions of both L and H chains have three
which is involved in placental transfer, complement fixa-
extremely variable (hypervariable) amino acid sequences
at the amino-terminal end that form the antigen-binding
activities (see Figure 59–2).
site (Figure 59–3). Only 5 to 10 amino acids in each hyper-
variable region form the antigen-binding site. Antigen–
antibody binding involves electrostatic and van der Waals’
forces and hydrogen and hydrophobic bonds rather than
IMMUNOGLOBULIN CLASSES
covalent bonds. The remarkable specificity of antibodies is
due to these hypervariable regions (see the discussion of
idiotypes on page 527).
Each IgG molecule consists of two L chains and two H
L chains belong to one of two types, κ (kappa) or λ
chains linked by disulfide bonds (molecular formula
(lambda), on the basis of amino acid differences in their IgG
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com the number and location of disulfide bonds. IgG1 makes up mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
H2L2). Because it has two identical antigen-binding sites, it
mebooksfree.com
constant regions. Both types occur in all classes of immu-
is said to be divalent. There are four subclasses, IgG1–
noglobulins (IgG, IgM, etc.), but any one immunoglobulin
2
IgG4, based on antigenic differences in the H chains and on
molecule contains only one type of L chain.
most (65%) of the total IgG. IgG2 antibody is directed
against polysaccharide antigens and is an important host
2
In humans, the ratio of immunoglobulins containing κ chains to those
defense against encapsulated bacteria.
containing λ chains is approximately 2:1.
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com