Page 540 - Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology ( PDFDrive )
P. 540
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com of the heavy-chain gene increases transcription of the 529 mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
CHAPTER 59 Antibodies
rearrangement. Each of these assembled V genes is then
transcribed with the appropriate C genes and spliced to
c-myc oncogene, which predisposes to malignancy.
produce an mRNA that codes for the complete peptide
chain. L and H chains are synthesized separately on poly-
somes and then assembled in the cytoplasm by means of
IMMUNOGLOBULIN CLASS
disulfide bonds to form H2L2 units. Finally, an oligosac-
charide is added to the constant region of the heavy chain,
Initially, all B cells carry IgM specific for an antigen and
and the immunoglobulin molecule is released from the cell.
The gene organization mechanism outlined above per- SWITCHING (ISOTYPE SWITCHING)
produce IgM antibody in response to exposure to that anti-
gen. Later, gene rearrangement permits the elaboration of
mits the assembly of a very large number of different mol-
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com genic specificity remains the same for the lifetime of the B mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
antibodies of the same antigenic specificity but of different
ecules. Antibody diversity depends on (1) multiple gene
immunoglobulin classes (Figure 59–6). Note that the anti-
segments, (2) their rearrangement into different sequences,
(3) the combining of different L and H chains in the assem-
cell and plasma cell because the specificity is determined by
bly of immunoglobulin molecules, and (4) mutations. A
fifth mechanism called junctional diversity applies primar-
the variable region genes (V, D, and J genes on the heavy
chain and V and J genes on the light chain) no matter
ily to the antibody heavy chain. Junctional diversity occurs
which heavy-chain constant region is being utilized.
by the addition of new nucleotides at the splice junctions
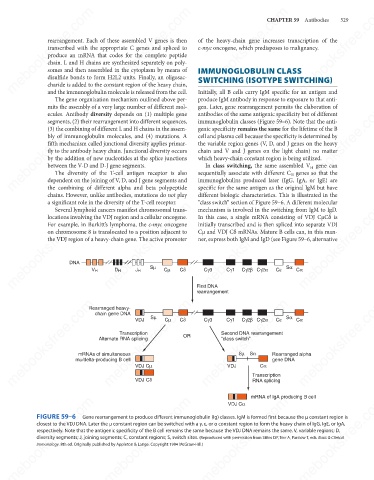
In class switching, the same assembled V gene can
between the V-D and D-J gene segments.
H
The diversity of the T-cell antigen receptor is also
H
immunoglobulins produced later (IgG, IgA, or IgE) are
dependent on the joining of V, D, and J gene segments and
specific for the same antigen as the original IgM but have
the combining of different alpha and beta polypeptide
different biologic characteristics. This is illustrated in the
chains. However, unlike antibodies, mutations do not play sequentially associate with different C genes so that the
“class switch” section of Figure 59–6. A different molecular
a significant role in the diversity of the T-cell receptor.
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com initially transcribed and is then spliced into separate VDJ mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
Several lymphoid cancers manifest chromosomal trans-
mechanism is involved in the switching from IgM to IgD.
locations involving the VDJ region and a cellular oncogene.
In this case, a single mRNA consisting of VDJ CμCδ is
For example, in Burkitt’s lymphoma, the c-myc oncogene
Cμ and VDJ Cδ mRNAs. Mature B cells can, in this man-
on chromosome 8 is translocated to a position adjacent to
the VDJ region of a heavy-chain gene. The active promoter
ner, express both IgM and IgD (see Figure 59–6, alternative
DNA
S
Sα
Cδ
C
Cγ3
J H
V H
D H
First DNA
rearrangement Cγ1 Cγ2β Cγ2α Cε Sα Cα
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com Alternate RNA splicing C Cδ OR Cγ3 Second DNA rearrangement Cα mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
Rearranged heavy-
chain gene DNA
S
Cε
Cγ2β Cγ2α
Cγ1
VDJ
Transcription
“class switch”
S
Sα
mRNAs of simultaneous
Rearranged alpha
gene DNA
mu/delta-producing B cell
Cα
VDJ C
VDJ
Transcription
VDJ Cδ
RNA splicing
mRNA of IgA producing B cell
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
VDJ Cα
FIGURE 59–6
Gene rearrangement to produce different immunoglobulin (Ig) classes. IgM is formed first because the μ constant region is
closest to the VDJ DNA. Later the μ constant region can be switched with a γ, ε, or α constant region to form the heavy chain of IgG, IgE, or IgA,
respectively. Note that the antigenic specificity of the B cell remains the same because the VDJ DNA remains the same. V, variable regions; D,
diversity segments; J, joining segments; C, constant regions; S, switch sites. (Reproduced with permission from Stites DP, Terr A, Parslow T, eds. Basic & Clinical
Immunology. 8th ed. Originally published by Appleton & Lange. Copyright 1994 McGraw-Hill.)
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com