Page 82 - Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology ( PDFDrive )
P. 82
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com CHAPTER 10 Antimicrobial Drugs: Mechanism of Action 71 mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
TABLE 10–2 Mechanism of Action of Important Antibacterial and Antifungal Drugs
Drugs
Mechanism of Action
Inhibition of cell wall synthesis
1. (a) Antibacterial activity inhibition of cross-linking (transpeptidation)
Penicillins, cephalosporins, imipenem, aztreonam, vancomycin
of peptidoglycan
(b) Inhibition of other steps in peptidoglycan synthesis
2. Antifungal activity inhibition of β-glucan synthesis
Caspofungin
Inhibition of protein synthesis Cycloserine, bacitracin
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com Sulfonamides, trimethoprim mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
Chloramphenicol, erythromycin, clindamycin, linezolid
Action on 50S ribosomal subunit
mebooksfree.com
Tetracyclines and aminoglycosides
Action on 30S ribosomal subunit
Inhibition of nucleic acid synthesis
Inhibition of nucleotide synthesis
Quinolones (e.g., ciprofloxacin)
Inhibition of DNA synthesis
Inhibition of mRNA synthesis
Rifampin
Alteration of cell membrane function
Antibacterial activity
Polymyxin, daptomycin
Antifungal activity
Amphotericin B, nystatin, terbinafine, azoles (e.g., itraconazole)
Other mechanisms of action
Isoniazid, metronidazole, ethambutol, pyrazinamide
1. Antibacterial activity
2. Antifungal activity
Griseofulvin, pentamidine
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com the peptidoglycan. Some bacteria (e.g., strains of S. aureus) mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
MECHANISMS OF ACTION
INHIBITION OF CELL WALL
are tolerant to the action of penicillin, because these auto-
SYNTHESIS
lytic enzymes are not activated. A tolerant organism is one
that is inhibited but not killed by a drug that is usually bac-
1. Inhibition of Bacterial
tericidal, such as penicillin (see page 90).
Cell Wall Synthesis
Penicillin-treated cells die by rupture as a result of the
Penicillins
Penicillins (and cephalosporins) act by inhibiting trans-
peptidases, the enzymes that catalyze the final cross-linking
step in the synthesis of peptidoglycan (see Figure 2–5). For influx of water into the high-osmotic-pressure interior of
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com Number of viable bacteria mebooksfree.com drug mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
example, in S. aureus, transpeptidation occurs between the
amino group on the end of the pentaglycine cross-link and
the terminal carboxyl group of the d-alanine on the tetra-
No drug
added
peptide side chain. Because the stereochemistry of penicil-
lin is similar to that of a dipeptide, d-alanyl-d-alanine,
Bacteriostatic
penicillin can bind to the active site of the transpeptidase
drug removed
and inhibit its activity.
Bacteriostatic
Drug
Two additional factors are involved in the action of
added
penicillin:
Bactericidal
(1) The first is that penicillin binds to a variety of recep-
drug
tors in the bacterial cell membrane and cell wall, called
Time
penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs). Some PBPs are trans-
peptidases; the others function in the synthesis of peptido-
mebooksfree.com
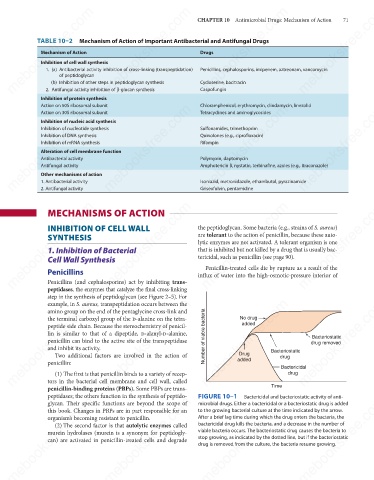
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com FIGURE 10–1 Bactericidal and bacteriostatic activity of anti- mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
glycan. Their specific functions are beyond the scope of
microbial drugs. Either a bactericidal or a bacteriostatic drug is added
this book. Changes in PBPs are in part responsible for an
to the growing bacterial culture at the time indicated by the arrow.
After a brief lag time during which the drug enters the bacteria, the
organism’s becoming resistant to penicillin.
bactericidal drug kills the bacteria, and a decrease in the number of
(2) The second factor is that autolytic enzymes called
viable bacteria occurs. The bacteriostatic drug causes the bacteria to
murein hydrolases (murein is a synonym for peptidogly-
stop growing, as indicated by the dotted line, but if the bacteriostatic
can) are activated in penicillin-treated cells and degrade
drug is removed from the culture, the bacteria resume growing.
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com