Page 87 - Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology ( PDFDrive )
P. 87
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com Ribosomal Subunit Mode of Action mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
PART I Basic Bacteriology
76
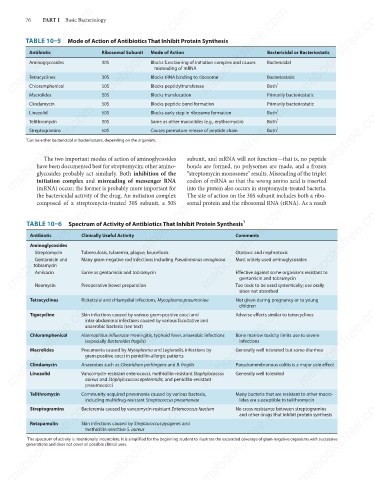
TABLE 10–5 Mode of Action of Antibiotics That Inhibit Protein Synthesis
Antibiotic
Bactericidal or Bacteriostatic
Aminoglycosides
Bactericidal
Blocks functioning of initiation complex and causes
30S
misreading of mRNA
Blocks tRNA binding to ribosome
Bacteriostatic
30S
Tetracyclines
1
Both
Blocks peptidyltransferase
Chloramphenicol
50S
50S
Primarily bacteriostatic
Blocks translocation
Macrolides
Clindamycin
Primarily bacteriostatic
Blocks peptide bond formation
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com 50S mebooksfree.com subunit, and mRNA will not function—that is, no peptide mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
1
Blocks early step in ribosome formation
50S
Linezolid
Both
1
50S
Same as other macrolides (e.g., erythromycin)
Both
Telithromycin
1
Causes premature release of peptide chain
Streptogramins
Both
50S
1
Can be either bactericidal or bacteriostatic, depending on the organism.
The two important modes of action of aminoglycosides
bonds are formed, no polysomes are made, and a frozen
have been documented best for streptomycin; other amino-
glycosides probably act similarly. Both inhibition of the
codon of mRNA so that the wrong amino acid is inserted
initiation complex and misreading of messenger RNA
(mRNA) occur; the former is probably more important for
into the protein also occurs in streptomycin-treated bacteria.
The site of action on the 30S subunit includes both a ribo-
the bactericidal activity of the drug. An initiation complex “streptomycin monosome” results. Misreading of the triplet
somal protein and the ribosomal RNA (rRNA). As a result
composed of a streptomycin-treated 30S subunit, a 50S
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
1
TABLE 10–6 Spectrum of Activity of Antibiotics That Inhibit Protein Synthesis
Clinically Useful Activity
Antibiotic
Comments
Aminoglycosides
Ototoxic and nephrotoxic
Tuberculosis, tularemia, plague, brucellosis
Streptomycin
Many gram-negative rod infections including Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Most widely used aminoglycosides
Gentamicin and
tobramycin
Same as gentamicin and tobramycin
Amikacin
Effective against some organisms resistant to
gentamicin and tobramycin
Preoperative bowel preparation
Neomycin
Too toxic to be used systemically; use orally
since not absorbed
Tetracyclines
Not given during pregnancy or to young
Rickettsial and chlamydial infections, Mycoplasma pneumoniae
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com pneumococci mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
children
Tigecycline
Adverse effects similar to tetracyclines
Skin infections caused by various gram-positive cocci and
intra-abdominal infections caused by various facultative and
anaerobic bacteria (see text)
Bone marrow toxicity limits use to severe
Haemophilus influenzae meningitis, typhoid fever, anaerobic infections
Chloramphenicol
infections
(especially Bacteroides fragilis)
Macrolides
Generally well tolerated but some diarrhea
Pneumonia caused by Mycoplasma and Legionella, infections by
gram-positive cocci in penicillin-allergic patients
Clindamycin
Anaerobes such as Clostridium perfringens and B. fragilis
Pseudomembranous colitis is a major side effect
Linezolid
aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis, and penicillin-resistant
Community-acquired pneumonia caused by various bacteria,
Telithromycin Vancomycin-resistant enterococci, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus Generally well tolerated
Many bacteria that are resistant to other macro-
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com methicillin-sensitive S. aureus mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
lides are susceptible to telithromycin
including multidrug-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae
Streptogramins
Bacteremia caused by vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium
No cross-resistance between streptogramins
and other drugs that inhibit protein synthesis
Retapamulin
Skin infections caused by Streptococcus pyogenes and
1
The spectrum of activity is intentionally incomplete. It is simplified for the beginning student to illustrate the expanded coverage of gram-negative organisms with successive
generations and does not cover all possible clinical uses.
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com