Page 91 - Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology ( PDFDrive )
P. 91
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com COOH SO NH 2 mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
80
PART I Basic Bacteriology
N
H N
NH
2
2
N
H C
2
2
3
NH 2 NH 2 H CO OCH 3 OCH 3
B
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com Para-aminobenzoic Dihydropteroate Dihydrofolic mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
A
Tetrahydrofolic
Dihydrofolate
acid
acid
acid
reductase
synthase
(THF)
(PABA)
(DHF)
+
Other
components
Inhibited
Inhibited
by
by
trimethoprim
sulfonamide
C
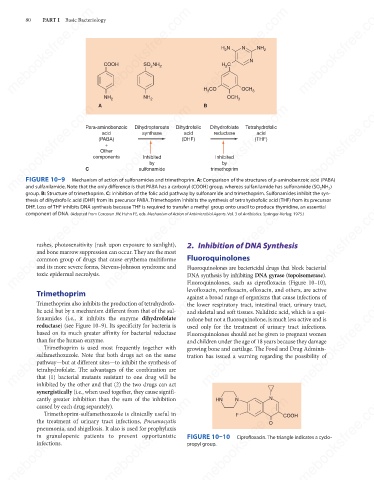
FIGURE 10–9
Mechanism of action of sulfonamides and trimethoprim. A: Comparison of the structures of p-aminobenzoic acid (PABA)
and sulfanilamide. Note that the only difference is that PABA has a carboxyl (COOH) group, whereas sulfanilamide has sulfonamide (SO 2 NH 2 )
group. B: Structure of trimethoprim. C: Inhibition of the folic acid pathway by sulfonamide and trimethoprim. Sulfonamides inhibit the syn-
thesis of dihydrofolic acid (DHF) from its precursor PABA. Trimethoprim inhibits the synthesis of tetrahydrofolic acid (THF) from its precursor
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com 2. Inhibition of DNA Synthesis mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
DHF. Loss of THF inhibits DNA synthesis because THF is required to transfer a methyl group onto uracil to produce thymidine, an essential
component of DNA. (Adapted from Corcoran JW, Hahn FE, eds. Mechanism of Action of Antimicrobial Agents. Vol. 3 of Antibiotics. Springer-Verlag; 1975.)
rashes, photosensitivity (rash upon exposure to sunlight),
and bone marrow suppression can occur. They are the most
Fluoroquinolones
common group of drugs that cause erythema multiforme
and its more severe forms, Stevens-Johnson syndrome and
Fluoroquinolones are bactericidal drugs that block bacterial
toxic epidermal necrolysis.
Fluoroquinolones, such as ciprofloxacin (Figure 10–10),
levofloxacin, norfloxacin, ofloxacin, and others, are active
Trimethoprim DNA synthesis by inhibiting DNA gyrase (topoisomerase).
against a broad range of organisms that cause infections of
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com nolone but not a fluoroquinolone, is much less active and is mebooksfree.com
Trimethoprim also inhibits the production of tetrahydrofo-
the lower respiratory tract, intestinal tract, urinary tract,
lic acid but by a mechanism different from that of the sul-
and skeletal and soft tissues. Nalidixic acid, which is a qui-
fonamides (i.e., it inhibits the enzyme dihydrofolate
reductase) (see Figure 10–9). Its specificity for bacteria is
used only for the treatment of urinary tract infections.
based on its much greater affinity for bacterial reductase
Fluoroquinolones should not be given to pregnant women
than for the human enzyme.
and children under the age of 18 years because they damage
Trimethoprim is used most frequently together with
growing bone and cartilage. The Food and Drug Adminis-
sulfamethoxazole. Note that both drugs act on the same
tration has issued a warning regarding the possibility of
pathway—but at different sites—to inhibit the synthesis of
tetrahydrofolate. The advantages of the combination are
that (1) bacterial mutants resistant to one drug will be
inhibited by the other and that (2) the two drugs can act
synergistically (i.e., when used together, they cause signifi- HN N N COOH
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com FIGURE 10–10 Ciprofloxacin. The triangle indicates a cyclo- mebooksfree.com
cantly greater inhibition than the sum of the inhibition
mebooksfree.com
caused by each drug separately).
Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole is clinically useful in
F
the treatment of urinary tract infections, Pneumocystis
O
pneumonia, and shigellosis. It also is used for prophylaxis
in granulopenic patients to prevent opportunistic
infections.
propyl group.
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com