Page 88 - Review of Medical Microbiology and Immunology ( PDFDrive )
P. 88
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com 2 mebooksfree.com CHAPTER 10 Antimicrobial Drugs: Mechanism of Action 77 mebooksfree.com
O
OH
R
OH
O
O
1
OH
NCR
HC
NH
C
2
NH
O
2
NH
OH
2
N(CH )
R H
O H
OH
R
R
2
3 2
O
H
NH
2
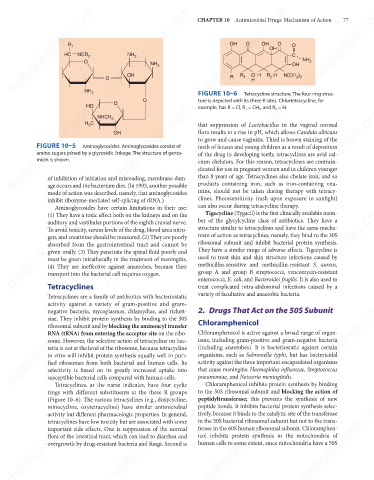
O FIGURE 10–6 1 Tetracycline structure. The four-ring struc-
ture is depicted with its three R sites. Chlortetracycline, for
O
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com 3 mebooksfree.com that suppression of Lactobacillus in the vaginal normal mebooksfree.com
HO
example, has R = Cl, R 1 = CH 3 , and R 2 = H.
NHCH
3
H C
flora results in a rise in pH, which allows Candida albicans
OH
to grow and cause vaginitis. Third is brown staining of the
FIGURE 10–5
Aminoglycosides. Aminoglycosides consist of
teeth of fetuses and young children as a result of deposition
amino sugars joined by a glycosidic linkage. The structure of genta-
of the drug in developing teeth; tetracyclines are avid cal-
micin is shown.
cium chelators. For this reason, tetracyclines are contrain-
dicated for use in pregnant women and in children younger
of inhibition of initiation and misreading, membrane dam-
products containing iron, such as iron-containing vita-
age occurs and the bacterium dies. (In 1993, another possible
mins, should not be taken during therapy with tetracy-
mode of action was described, namely, that aminoglycosides
clines. Photosensitivity (rash upon exposure to sunlight)
inhibit ribozyme-mediated self-splicing of rRNA.) than 8 years of age. Tetracyclines also chelate iron, and so
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com structure similar to tetracyclines and have the same mecha- mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
can also occur during tetracycline therapy.
Aminoglycosides have certain limitations in their use:
Tigecycline (Tygacil) is the first clinically available mem-
(1) They have a toxic effect both on the kidneys and on the
ber of the glycylcycline class of antibiotics. They have a
auditory and vestibular portions of the eighth cranial nerve.
To avoid toxicity, serum levels of the drug, blood urea nitro-
nism of action as tetracyclines; namely, they bind to the 30S
gen, and creatinine should be measured. (2) They are poorly
ribosomal subunit and inhibit bacterial protein synthesis.
absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and cannot be
They have a similar range of adverse effects. Tigecycline is
given orally. (3) They penetrate the spinal fluid poorly and
used to treat skin and skin structure infections caused by
must be given intrathecally in the treatment of meningitis.
methicillin-sensitive and methicillin-resistant S. aureus,
(4) They are ineffective against anaerobes, because their
transport into the bacterial cell requires oxygen.
enterococci, E. coli, and Bacteroides fragilis. It is also used to
Tetracyclines
treat complicated intra-abdominal infections caused by a
variety of facultative and anaerobic bacteria.
Tetracyclines are a family of antibiotics with bacteriostatic group A and group B streptococci, vancomycin-resistant
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com Chloramphenicol mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
activity against a variety of gram-positive and gram-
2. Drugs That Act on the 50S Subunit
negative bacteria, mycoplasmas, chlamydiae, and rickett-
siae. They inhibit protein synthesis by binding to the 30S
ribosomal subunit and by blocking the aminoacyl transfer
Chloramphenicol is active against a broad range of organ-
RNA (tRNA) from entering the acceptor site on the ribo-
isms, including gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria
some. However, the selective action of tetracycline on bac-
(including anaerobes). It is bacteriostatic against certain
teria is not at the level of the ribosome, because tetracycline
organisms, such as Salmonella typhi, but has bactericidal
in vitro will inhibit protein synthesis equally well in puri-
activity against the three important encapsulated organisms
fied ribosomes from both bacterial and human cells. Its
selectivity is based on its greatly increased uptake into
pneumoniae, and Neisseria meningitidis.
susceptible bacterial cells compared with human cells.
Chloramphenicol inhibits protein synthesis by binding
Tetracyclines, as the name indicates, have four cyclic
to the 50S ribosomal subunit and blocking the action of
rings with different substituents at the three R groups that cause meningitis: Haemophilus influenzae, Streptococcus
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com in the 50S bacterial ribosomal subunit but not to the trans- mebooksfree.com
peptidyltransferase; this prevents the synthesis of new
(Figure 10–6). The various tetracyclines (e.g., doxycycline,
peptide bonds. It inhibits bacterial protein synthesis selec-
minocycline, oxytetracycline) have similar antimicrobial
tively, because it binds to the catalytic site of the transferase
activity but different pharmacologic properties. In general,
tetracyclines have low toxicity but are associated with some
ferase in the 60S human ribosomal subunit. Chloramphen-
important side effects. One is suppression of the normal
icol inhibits protein synthesis in the mitochondria of
flora of the intestinal tract, which can lead to diarrhea and
human cells to some extent, since mitochondria have a 50S
overgrowth by drug-resistant bacteria and fungi. Second is
mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com mebooksfree.com