Page 556 - 9780077418427.pdf
P. 556
/Volume/201/MHDQ233/tat78194_disk1of1/0073378194/tat78194_pagefile
tiL12214_ch21_521-540.indd Page 533 9/23/10 11:10 AM user-f465
tiL12214_ch21_521-540.indd Page 533 9/23/10 11:10 AM user-f465 /Volume/201/MHDQ233/tat78194_disk1of1/0073378194/tat78194_pagefiles
SOLUTION
Cenozoic era Faunal assemblage problems are solved by comparing the age ranges
of each of the life-forms and determining the geologic time in which
Mesozoic era the age ranges overlap. This can be visualized by creating a table that
lists the geologic periods encompassing the age ranges of all of the
Paleozoic era
life-forms present in the assemblage and shading the age range of each
Precambrian life-form. In this case, the three life-forms could have only co-existed
during the Late Ordovician through Early Silurian.
Geologic Trilobite Brachiopod Mollusk
Period
Pennsylvanian
Cambrian Mississippian
Ordovician Devonian
Late
Silurian Silurian Ordovician
Devonian Ordovician through Early
Mississippian Cambrian Silurian
Pennsylvanian
Permian
EXAMPLE 21.4
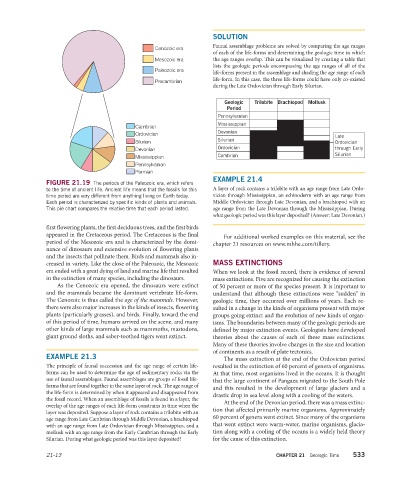
FIGURE 21.19 The periods of the Paleozoic era, which refers
to the time of ancient life. Ancient life means that the fossils for this A layer of rock contains a trilobite with an age range from Late Ordo-
time period are very different from anything living on Earth today. vician through Mississippian, an echinoderm with an age range from
Each period is characterized by specific kinds of plants and animals. Middle Ordovician through Late Devonian, and a brachiopod with an
This pie chart compares the relative time that each period lasted. age range from the Late Devonian through the Mississippian. During
what geologic period was this layer deposited? (Answer: Late Devonian.)
first flowering plants, the first deciduous trees, and the first birds
appeared in the Cretaceous period. The Cretaceous is the final For additional worked examples on this material, see the
period of the Mesozoic era and is characterized by the domi- chapter 21 resources on www.mhhe.com/tillery.
nance of dinosaurs and extensive evolution of flowering plants
and the insects that pollinate them. Birds and mammals also in-
creased in variety. Like the close of the Paleozoic, the Mesozoic MASS EXTINCTIONS
era ended with a great dying of land and marine life that resulted When we look at the fossil record, there is evidence of several
in the extinction of many species, including the dinosaurs. mass extinctions. Five are recognized for causing the extinction
As the Cenozoic era opened, the dinosaurs were extinct of 50 percent or more of the species present. It is important to
and the mammals became the dominant vertebrate life-form. understand that although these extinctions were “sudden” in
The Cenozoic is thus called the age of the mammals. However, geologic time, they occurred over millions of years. Each re-
there were also major increases in the kinds of insects, flowering sulted in a change in the kinds of organisms present with major
plants (particularly grasses), and birds. Finally, toward the end groups going extinct and the evolution of new kinds of organ-
of this period of time, humans arrived on the scene, and many isms. The boundaries between many of the geologic periods are
other kinds of large mammals such as mammoths, mastodons, defined by major extinction events. Geologists have developed
giant ground sloths, and saber-toothed tigers went extinct. theories about the causes of each of these mass extinctions.
Many of these theories involve changes in the size and location
of continents as a result of plate tectonics.
EXAMPLE 21.3 The mass extinction at the end of the Ordovician period
The principle of faunal succession and the age range of certain life- resulted in the extinction of 60 percent of genera of organisms.
forms can be used to determine the age of sedimentary rocks via the At that time, most organisms lived in the oceans. It is thought
use of faunal assemblages. Faunal assemblages are groups of fossil life- that the large continent of Pangaea migrated to the South Pole
forms that are found together in the same layer of rock. The age range of
and this resulted in the development of large glaciers and a
the life-form is determined by when it appeared and disappeared from
drastic drop in sea level along with a cooling of the waters.
the fossil record. When an assemblage of fossils is found in a layer, the
At the end of the Devonian period, there was a mass extinc-
overlap of the age ranges of each life-form constrains in time when the
tion that affected primarily marine organisms. Approximately
layer was deposited. Suppose a layer of rock contains a trilobite with an
60 percent of genera went extinct. Since many of the organisms
age range from Late Cambrian through Middle Devonian, a brachiopod
with an age range from Late Ordovician through Mississippian, and a that went extinct were warm-water, marine organisms, glacia-
mollusk with an age range from the Early Cambrian through the Early tion along with a cooling of the oceans is a widely held theory
Silurian. During what geologic period was this layer deposited? for the cause of this extinction.
21-13 CHAPTER 21 Geologic Time 533