Page 32 - PRE-U STPM BIOLOGY TERM 1
P. 32
Biology Term 1 STPM Chapter 2 Structure of Cells and Organelles
7. Their content is acidic, homogenous in nature and contain many
types of hydrolases. They include proteinase, lipase, carbohydratase,
acid nuclease (DNase and RNase) and acid phosphatase.
8. The functions of lysosomes are as follows:
(a) It can digest foreign substances or cells that are endocytosised.
(b) It clips certain bond such as that of thyroglobulin. Thyroglobulin
is formed within the follicle of the thyroid gland. When it passes 2
through cells lining the follicle, thyroxin is released from the
globulin and emptied into the capillary.
(c) It can carry out autophagy i.e. old or worn out organelles are
digested by their digestive enzymes. Red blood cells have their
nuclei digested during their course of development in bone
marrows.
(d) It exports their enzymes by exocytosis such as in the cartilage by
osteoclasts during its development to form bones.
(e) It can carry out autolysis in which the whole cells are digested for
rebuilding of new tissue during metamorphorsis. This happens
in the tail of the tadpole where the digestion products are used
for building lungs and adult skin.
Ribosomes
1. Ribosomes are small granules where synthesis of proteins occurs.
2. They are found in all cells particularly cells that produce a lot of
proteins such as the glandular cells of pancreas and liver. Ribosomes
are found in the nucleus, free in cytoplasm or in cytoplasm attached
to ER, mitochondria and chloroplasts.
3. Their number is not fixed. It is found in large numbers in the
glandular cell that produces a lot of proteins and its numbers can
increase.
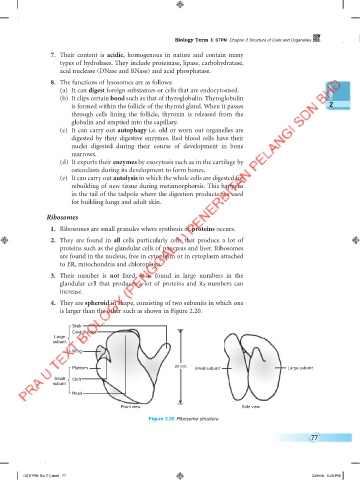
4. They are spheroid in shape, consisting of two subunits in which one
is larger than the other such as shown in Figure 2.20.
Stalk
Central ridge
Large
subunit
Wing
Platform 20 nm Small subunit Large subunit
Small Cleft
subunit
Head
Front view Side view
Figure 2.20 Ribosome structure
77
02[STPM Bio T1].indd 77 3/29/18 5:08 PM