Page 36 - PRE-U STPM BIOLOGY TERM 1
P. 36
Biology Term 1 STPM Chapter 2 Structure of Cells and Organelles
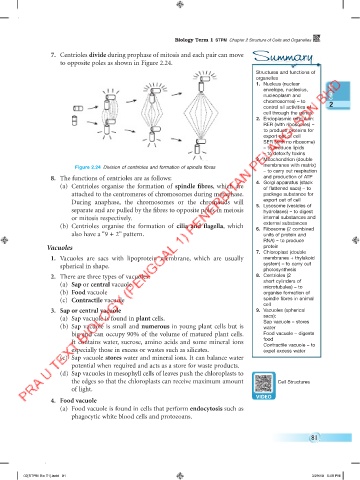
7. Centrioles divide during prophase of mitosis and each pair can move Summary
to opposite poles as shown in Figure 2.24.
Structures and functions of
organelles
1. Nucleus (nuclear
envelope, nucleolus,
nucleoplasm and
chromosomes) – to 2
control all activities of
cell through the genes.
2. Endoplasmic reticulum:
RER (with ribosomes) –
to produce proteins for
export out of cell
SER (with no ribosome)
– to produce lipids
– to detoxify toxins
3. Mitochondrion (double
membranes with matrix)
Figure 2.24 Division of centrioles and formation of spindle fibres
– to carry out respiration
8. The functions of centrioles are as follows: and production of ATP
(a) Centrioles organise the formation of spindle fibres, which are 4. Golgi apparatus (stack
of flattened sacs) – to
attached to the centromeres of chromosomes during metaphase. package substance for
export out of cell
During anaphase, the chromosomes or the chromatids will 5. Lysosome (vesicles of
separate and are pulled by the fibres to opposite poles in meiosis hydrolases) – to digest
or mitosis respectively. internal substances and
(b) Centrioles organise the formation of cilia and flagella, which external substances
6. Ribosome (2 combined
also have a “9 + 2” pattern. units of protein and
RNA) – to produce
Vacuoles protein
7. Chloroplast (double
1. Vacuoles are sacs with lipoprotein membrane, which are usually membranes + thylakoid
spherical in shape. system) – to carry out
photosynthesis
2. There are three types of vacuoles: 8. Centrioles (2
(a) Sap or central vacuole short cylinders of
microtubules) – to
(b) Food vacuole organise formation of
(c) Contractile vacuole spindle fibres in animal
cell
3. Sap or central vacuole 9. Vacuoles (spherical
(a) Sap vacuole is found in plant cells. sacs):
Sap vacuole – stores
(b) Sap vacuole is small and numerous in young plant cells but is water
big and can occupy 90% of the volume of matured plant cells. Food vacuole – digests
It contains water, sucrose, amino acids and some mineral ions food
Contractile vacuole – to
especially those in excess or wastes such as silicates. expel excess water
(c) Sap vacuole stores water and mineral ions. It can balance water
potential when required and acts as a store for waste products.
(d) Sap vacuoles in mesophyll cells of leaves push the chloroplasts to
the edges so that the chloroplasts can receive maximum amount Cell Structures
of light.
VIDEO
4. Food vacuole
(a) Food vacuole is found in cells that perform endocytosis such as
phagocytic white blood cells and protozoans.
81
02[STPM Bio T1].indd 81 3/29/18 5:08 PM