Page 28 - PRE-U STPM BIOLOGY TERM 1
P. 28
Biology Term 1 STPM Chapter 2 Structure of Cells and Organelles
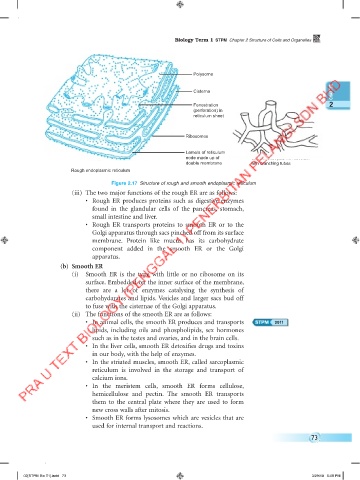
Polysome
Cisterna
Fenestration 2
(perforation) in
reticulum sheet
Ribosomes
Lamela of reticulum
node made up of Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
double membrane with branching tubes
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Figure 2.17 Structure of rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulum
(iii) The two major functions of the rough ER are as follows:
• Rough ER produces proteins such as digestive enzymes
found in the glandular cells of the pancreas, stomach,
small intestine and liver.
• Rough ER transports proteins to smooth ER or to the
Golgi apparatus through sacs pinched off from its surface
membrane. Protein like mucus has its carbohydrate
component added in the smooth ER or the Golgi
apparatus.
(b) Smooth ER
(i) Smooth ER is the type with little or no ribosome on its
surface. Embedded on the inner surface of the membrane,
there are a lot of enzymes catalysing the synthesis of
carbohydarates and lipids. Vesicles and larger sacs bud off
to fuse with the cisternae of the Golgi apparatus.
(ii) The functions of the smooth ER are as follows:
• In animal cells, the smooth ER produces and transports 2011
lipids, including oils and phospholipids, sex hormones
such as in the testes and ovaries, and in the brain cells.
• In the liver cells, smooth ER detoxifies drugs and toxins
in our body, with the help of enzymes.
• In the striated muscles, smooth ER, called sarcoplasmic
reticulum is involved in the storage and transport of
calcium ions.
• In the meristem cells, smooth ER forms cellulose,
hemicellulose and pectin. The smooth ER transports
them to the central plate where they are used to form
new cross walls after mitosis.
• Smooth ER forms lysosomes which are vesicles that are
used for internal transport and reactions.
73
02[STPM Bio T1].indd 73 3/29/18 5:08 PM