Page 38 - PRE-U STPM BIOLOGY TERM 1
P. 38
Biology Term 1 STPM Chapter 2 Structure of Cells and Organelles
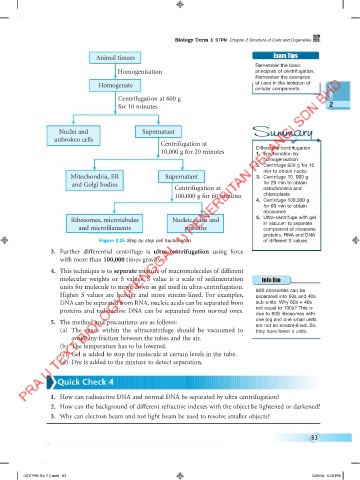
Animal tissues Exam Tips
Remember the basic
Homogenisation principles of centrifugation.
Remember the examples
Homogenate of uses in the isolation of
cellular components.
Centrifugation at 600 g
for 10 minutes 2
Nuclei and Supernatant Summary
unbroken cells
Centrifugation at
10,000 g for 20 minutes Differential centrifugation
1. Fractionation by
homogenisation
2. Centrifuge 600 g for 10
min to obtain nuclei
Mitochondria, ER Supernatant 3. Centrifuge 10, 000 g
and Golgi bodies for 20 min to obtain
Centrifugation at mitochondria and
100,000 g for 60 minutes chloroplasts
4. Centrifuge 100,000 g
for 60 min to obtain
ribosomes
Ribosomes, microtubules Nucleic acids and 5. Ultra-centrifuge with gel
in vacuum to separate
and microfilaments proteins component of ribosome
proteins, RNA and DNA
Figure 2.25 Step by step cell fractionation of different S values
3. Further differential centrifuge is ultra-centrifugation using force
with more than 100,000 times gravity.
4. This technique is to separate mixture of macromolecules of different
molecular weights or S values. S value is a scale of sedimentation Info Bio
units for molecule to move down in gel used in ultra-centrifugation.
Higher S values are heavier and more stream-lined. For examples, 80S ribosomes can be
separated into 60s and 40s
DNA can be separated from RNA, nucleic acids can be separated from sub-units. Why 60s + 40s
not equal to 100s? This is
proteins and radioactive DNA can be separated from normal ones. due to 80S ribosomes with
one big and one small units
5. The method and precautions are as follows: are not so stream-lined. So,
(a) The space within the ultracentrifuge should be vacuumed to they have lower s units.
avoid any friction between the tubes and the air.
(b) The temperature has to be lowered.
(c) Gel is added to stop the molecule at certain levels in the tube.
(d) Dye is added to the mixture to detect separation.
Quick Check 4
1. How can radioactive DNA and normal DNA be separated by ultra centrifugation?
2. How can the background of different refractive indexes with the object be lightened or darkened?
3. Why can electron beam and not light beam be used to resolve smaller objects?
83
02[STPM Bio T1].indd 83 3/29/18 5:08 PM