Page 49 - PRE-U STPM BIOLOGY TERM 1
P. 49
Biology Term 1 STPM Chapter 2 Structure of Cells and Organelles
Summary
Epithelial tissues
Covering epithelia
1. Simple squamous
• for absorption in
endothelium and alveoli
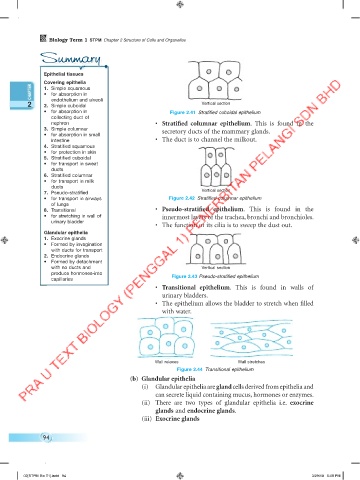
2 2. Simple cuboidal Vertical section
• for absorption in Figure 2.41 Stratified cuboidal epithelium
collecting duct of
nephron • Stratified columnar epithelium. This is found in the
3. Simple columnar secretory ducts of the mammary glands.
• for absorption in small
intestine • The duct is to channel the milkout.
4. Stratified squamous
• for protection in skin
5. Stratified cuboidal
• for transport in sweat
ducts
6. Stratified columnar
• for transport in milk
ducts
7. Pseudo-stratified Vertical section
• for transport in airways Figure 2.42 Stratified columnar epithelium
of lungs
8. Transitional • Pseudo-stratified epithelium. This is found in the
• for stretching in wall of innermost layers of the trachea, bronchi and bronchioles.
urinary bladder
• The function of its cilia is to sweep the dust out.
Glandular epithelia
1. Exocrine glands
• Formed by invagination
with ducts for transport
2. Endocrine glands
• Formed by detachment
with no ducts and Vertical section
produce hormones-into
capillaries Figure 2.43 Pseudo-stratified epithelium
• Transitional epithelium. This is found in walls of
urinary bladders.
• The epithelium allows the bladder to stretch when filled
with water.
Wall relaxes Wall stretches
Figure 2.44 Transitional epithelium
(b) Glandular epithelia
(i) Glandular epithelia are gland cells derived from epithelia and
can secrete liquid containing mucus, hormones or enzymes.
(ii) There are two types of glandular epithelia i.e. exocrine
glands and endocrine glands.
(iii) Exocrine glands
94
02[STPM Bio T1].indd 94 3/29/18 5:08 PM