Page 44 - PRE-U STPM BIOLOGY TERM 1
P. 44
Biology Term 1 STPM Chapter 2 Structure of Cells and Organelles
3. Xylem consists of four types of cells, namely vessels, tracheids,
parenchyma and sclerenchyma.
(a) Vessels
(i) These are the largest cells and are shaped like vessels.
(ii) Their ends slant, open and connect to one another to form
long pipes.
(iii) They are dead cells with hollow lumen and no cross walls 2
when mature.
(iv) They have secondary wall impregnated with lignin.
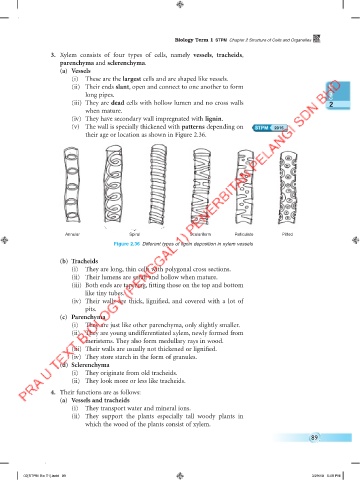
(v) The wall is specially thickened with patterns depending on 2015
their age or location as shown in Figure 2.36.
Annular Spiral Scalariform Reticulate Pitted
Figure 2.36 Different types of lignin deposition in xylem vessels
(b) Tracheids
(i) They are long, thin cells with polygonal cross sections.
(ii) Their lumens are small and hollow when mature.
(iii) Both ends are tapering, fitting those on the top and bottom
like tiny tubes.
(iv) Their walls are thick, lignified, and covered with a lot of
pits.
(c) Parenchyma
(i) They are just like other parenchyma, only slightly smaller.
(ii) They are young undifferentiated xylem, newly formed from
meristems. They also form medullary rays in wood.
(iii) Their walls are usually not thickened or lignified.
(iv) They store starch in the form of granules.
(d) Sclerenchyma
(i) They originate from old tracheids.
(ii) They look more or less like tracheids.
4. Their functions are as follows:
(a) Vessels and tracheids
(i) They transport water and mineral ions.
(ii) They support the plants especially tall woody plants in
which the wood of the plants consist of xylem.
89
02[STPM Bio T1].indd 89 3/29/18 5:08 PM