Page 8 - PRE-U STPM BIOLOGY TERM 1
P. 8
Biology Term 1 STPM Chapter 2 Structure of Cells and Organelles
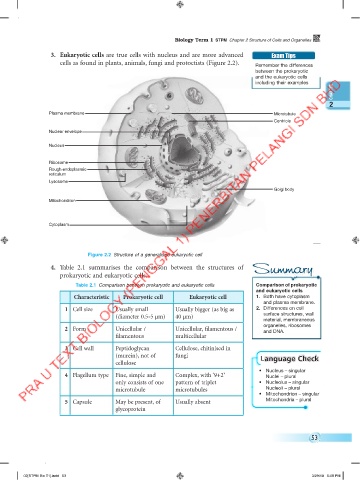
3. Eukaryotic cells are true cells with nucleus and are more advanced Exam Tips
cells as found in plants, animals, fungi and protoctists (Figure 2.2). Remember the differences
between the prokaryotic
and the eukaryotic cells
including their examples
2
Plasma membrane Microtubule
Centriole
Nuclear envelope
Nucleus
Ribosome
Rough endoplasmic
reticulum
Lysosome
Golgi body
Mitochondrion
Cytoplasm
Figure 2.2 Structure of a generalised eukaryotic cell
4. Table 2.1 summarises the comparison between the structures of Summary
prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Table 2.1 Comparison between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Comparison of prokaryotic
and eukaryotic cells
Characteristic Prokaryotic cell Eukaryotic cell 1. Both have cytoplasm
and plasma membrane.
1 Cell size Usually small Usually bigger (as big as 2. Differences on cell
Language Check
Language Check
(diameter 0.5-5 µm) 40 µm) surface structures, wall
material, membraneous
organelles, ribosomes
2 Form Unicellular / Unicellular, filamentous / and DNA.
filamentous multicellular
3 Cell wall Peptidoglycan Cellulose, chitinised in
(murein), not of fungi Language Check
Language Check
cellulose
• Nucleus – singular
4 Flagellum type Fine, simple and Complex, with ‘9+2’ Nuclei – plural
only consists of one pattern of triplet • Nucleolus – singular
microtubule microtubules Nucleoli – plural
• Mitochondrion – singular
5 Capsule May be present, of Usually absent Mitochondria – plural
glycoprotein
53
02[STPM Bio T1].indd 53 3/29/18 5:08 PM