Page 12 - PRE-U STPM BIOLOGY TERM 1
P. 12
Biology Term 1 STPM Chapter 2 Structure of Cells and Organelles
(iii) The uses of compound microscopes are as follows:
• Compound microscopes can be used to observe objects
smaller than 0.1 mm.
• The invention of microscopes led to the formulation of
the cell theory, which states that all organisms are made
of cells.
• Observation of microscopes also proves that 2
microorganisms cause diseases.
(iv) They have the following limitations:
• Objects have to be sectioned into thin slices, fixed and
stained before they can be observed. This makes the
study of living cells difficult as they have to be killed.
• The resolution limit of light microscope is 0.2 µm,
meaning that any object smaller than that cannot be seen
clearly.
(b) Phase contrast microscopes
(i) These are compound microscopes that can adjust the
contrast of the object against the background, either
darkened or lightened. Living cells can be observed without
staining.
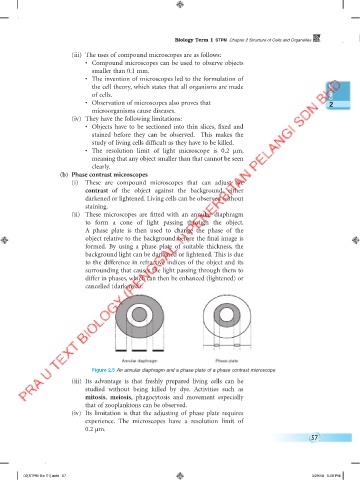
(ii) These microscopes are fitted with an annular diaphragm
to form a cone of light passing through the object.
A phase plate is then used to change the phase of the
object relative to the background before the final image is
formed. By using a phase plate of suitable thickness, the
background light can be darkened or lightened. This is due
to the difference in refractive indices of the object and its
surrounding that causes the light passing through them to
differ in phases, which can then be enhanced (lightened) or
cancelled (darkened).
Annular diaphragm Phase plate
Figure 2.5 An annular diaphragm and a phase plate of a phase contrast microscope
(iii) Its advantage is that freshly prepared living cells can be
studied without being killed by dye. Activities such as
mitosis, meiosis, phagocytosis and movement especially
that of zooplanktons can be observed.
(iv) Its limitation is that the adjusting of phase plate requires
experience. The microscopes have a resolution limit of
0.2 µm.
57
02[STPM Bio T1].indd 57 3/29/18 5:08 PM