Page 22 - PRE-U STPM CHEMISTRY TERM 1
P. 22
Chemistry Term 1 STPM
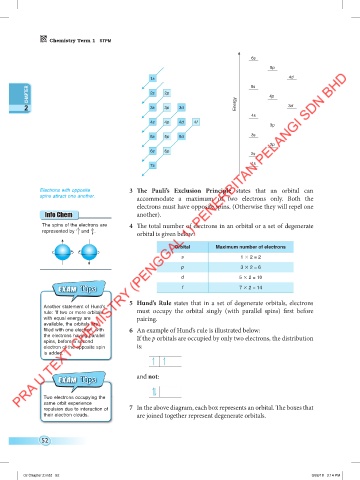
6s
5p
4d
1s
CHAPTER 2s 2p 5s 4p
2 3s 3p 3d Energy 3d
4s
4s 4p 4d 4f
3p
3s
5s 5p 5d
2p
6s 6p
2s
1s
7s
Electrons with opposite 3 The Pauli’s Exclusion Principle states that an orbital can
accommodate a maximum of two electrons only. Both the
spins attract one another.
electrons must have opposite spins. (Otherwise they will repel one
Info Chem another).
T
Tips
ips
The spins of the electrons are 4 The total number of electrons in an orbital or a set of degenerate
Exam
Exam ’ and ‘ ’.
represented by ‘
orbital is given below:
Orbital Maximum number of electrons
s 1 2 = 2
p 3 2 = 6
d 5 2 = 10
ips
T
ips
T
Tips
Exam Tips f 7 2 = 14
Exam
Exam
Exam
5 Hund’s Rule states that in a set of degenerate orbitals, electrons
Another statement of Hund's
rule: 'If two or more orbitals must occupy the orbital singly (with parallel spins) first before
with equal energy are pairing.
available, the orbitals are
filled with one electron, with 6 An example of Hund’s rule is illustrated below:
the electrons having parallel If the p orbitals are occupied by only two electrons, the distribution
spins, before a second
electron of the opposite spin is:
is added.'
T
ips
Exam Tips and not:
Exam
Two electrons occupying the
same orbit experience
repulsion due to interaction of 7 In the above diagram, each box represents an orbital. The boxes that
their electron clouds. are joined together represent degenerate orbitals.
52
02 Chapter 2.indd 52 3/26/18 3:14 PM