Page 36 - PRE-U STPM CHEMISTRY TERM 1
P. 36
Chemistry Term 1 STPM
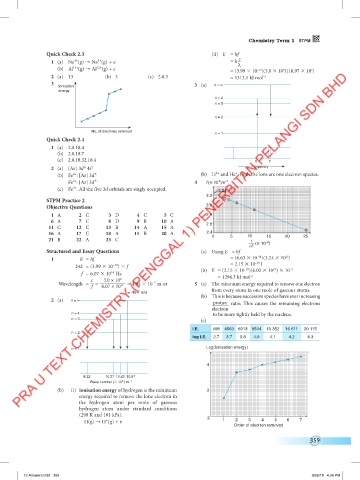
Quick Check 2.3 (ii) E = hf
4+
5+
1 (a) Na (g) → Na (g) + e = h λ c
(b) Al 11+ (g) → Al 12+ (g) + e = (3.99 10 )(3.0 10 )(10.97 10 )
–13
8
6
2 (a) 13 (b) 3 (c) 2.8.3 = 1313.1 kJ mol
–1
3
Ionisation 3 (a) n = ∞
energy
n = 4
n = 3
n = 2
No. of electrons removed
n = 1
Quick Check 2.4
1 (a) 2.8.18.4
(b) 2.8.18.7
(c) 2.8.18.32.18.4 X Y
6
2 (a) [Ar] 3d 4s 2 Frequency
+
2+
2+
(b) Fe : [Ar] 3d 6 (b) Li and He . Both the ions are one electron species.
Fe : [Ar] 3d 5 4 f (× 10 )/s –1
3+
5
3+
(c) Fe . All the five 3d orbitals are singly occupied. 3.24
3.2
STPM Practice 2
Objective Questions 3.0
1 A 2 C 3 D 4 C 5 C 2.8
6 A 7 C 8 D 9 B 10 A 2.6
11 C 12 C 13 B 14 A 15 A
16 A 17 C 18 A 19 B 20 A 2.4 0 10
21 B 22 A 23 C 5 1 –2 15 20 25
n 2 (× 10 )
Structured and Essay Questions (a) Using E = hf
–34
1 E = hf = (6.63 10 )(3.24 10 )
15
–18
242 = (3.99 10 ) f = 2.15 10 J
–13
23
–18
f = 6.07 10 Hz (b) E = (2.15 10 )(6.02 10 ) 10 –3
14
–1
c 3.0 × 10 8 = 1294.3 kJ mol
–7
Wavelength = = 6.07 × 10 14 = 4.94 10 m or 5 (a) The minimum energy required to remove one electron
f
from every atom in one mole of gaseous atoms.
= 494 nm (b) This is because successive species have ever increasing
2 (a) n = ∞
proton ratio. This causes the remaining electrons
electron
n = 4 to be more tightly held by the nucleus.
(c)
n = 3
I.E. 496 4563 6913 9544 13 352 16 611 20 115
n = 2
log I.E. 2.7 3.7 3.8 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3
n = 1 Log(ionisation energy)
4
8.22 10.27 10.62 10.97
Wave number ( 10 6 ) m –1
(b) (i) Ionisation energy of hydrogen is the minimum 3
energy required to remove the lone electron in
the hydrogen atom per mole of gaseous
hydrogen atom under standard conditions
(298 K and 101 kPa).
2
H(g) → H (g) + e 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
+
Order of electron removed
359
12 Answers.indd 359 3/26/18 4:06 PM