Page 39 - PRE-U STPM CHEMISTRY TERM 1
P. 39
Chemistry Term 1 STPM
4 1-propanol. It is bigger and has more electrons than (b) NH and H O have intermolecular hydrogen
3
2
ethanol. bonding while weak van der Waals forces exist
Quick Check 3.9 between CH molecules. This accounts for the
4
higher boiling point of NH and H O.
2
3
1 CH COOH. The large non-polar C H group in H O has two lone pair of electrons compared to
5
3
6
C H COOH decreases the solubility of benzoic acid. 2
6 5 only one for NH . Thus, H O can form more
2
3
2 1,2,3-propantriol has three —OH group. As a result, it intermolecular hydrogen bonding with one another.
can form more hydrogen bonds with water molecule On top of that, oxygen being more electronegative
compared to ethanol. than nitrogen forms stronger hydrogen bonds.
3 C H OH. It can form hydrogen bonds with water (c)
2
5
molecules, but C H SH cannot. HC—(CHOH) —CH —O—H
4
2
2 5 ||
4 (C H ) N cannot form hydrogen bonds with water O
5 3
2
because there are no hydrogen atoms attached directly to H H
the nitrogen atom.
5 NH can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules, but O
3
PH cannot.
3
3 (a) (i) HCl is polar but CO is non-polar.
2
STPM Practice 3 (ii) Intermolecular forces between NH molecules
3
Objective Questions are the hydrogen bonds.
1 C 2 C 3 B 4 B 5 C Weak intermolecular van der Waals forces exist
6 A 7 D 8 D 9 B 10 D between HCl molecules
11 B 12 B 13 D 14 A 15 C (b) NH can form hydrogen bonds with water
3
16 B 17 B 18 C 19 D 20 D molecules.
21 C 22 A 23 B 24 C 25 D HCl reacts with water to form water-soluble ions:
+
26 C 27 D 28 B 29 C 30 C HCl(g) + H O(l) → H O (aq) + Cl (aq)
–
3
2
31 B 32 C 33 D 34 D 35 B CO is non-polar.
2
36 B 37 C 38 D 39 A 40 C 4 (a)
41 C 42 C
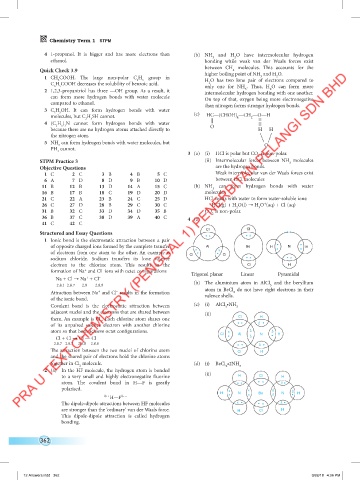
Structured and Essay Questions Cl Cl x x
x • x •
1 Ionic bond is the electrostatic attraction between a pair
of opposite charged ions formed by the complete transfer Al Be H • x N • x H
of electrons from one atom to the other. An example is Cl • x • x Cl
sodium chloride. Sodium transfers its lone valence x • x •
electron to the chlorine atom. This results in the Cl H
–
+
formation of Na and Cl ions with octet configurations Trigonal planar Linear Pyramidal
Na + Cl → Na + Cl –
+
2.8.1 2.8.7 2.8 2.8.8 (b) The aluminium atom in AlCl and the beryllium
3
atom in BeCl do not have eight electrons in their
–
+
Attraction between Na and Cl results in the formation valence shells. 2
of the ionic bond.
Covalent bond is the electrostatic attraction between (c) (i) AlCl •NH 3
3
adjacent nuclei and the electrons that are shared between
(ii)
them. An example is Cl . Each chlorine atom shares one Cl H
2
of its unpaired valence electron with another chlorine x • •
atom so that both achieve octet configurations. x
Cl + Cl → Cl — Cl Cl • Al N • H
2.8.7 2.8.7 2.8.8 2.8.8 x • •
The attraction between the two nuclei of chlorine atom Cl H
and the shared pair of electrons hold the chlorine atoms
together in Cl molecule. (d) (i) BeCl •2NH
2 2 3
2 (a) In the HF molecule, the hydrogen atom is bonded
to a very small and highly electronegative fluorine (ii) H Cl H
atom. The covalent bond in H—F is greatly x • • x •
polarised. x
H • N Be N H
δ ++ H—F δ–– x x •
The dipole-dipole attractions between HF molecules x • • x •
are stronger than the ‘ordinary’ van der Waals force. H Cl H
This dipole-dipole attraction is called hydrogen
bonding.
362
12 Answers.indd 362 3/26/18 4:06 PM