Page 41 - PRE-U STPM CHEMISTRY TERM 1
P. 41
Chemistry Term 1 STPM
(c) The intermolecular forces between the HCl (ii) Hydrogen chloride is a covalent compound that
molecules, the HBr molecules and the HI molecules exists as the simple HCl molecules with strong
are the weak van der Waals forces. The strength of covalent bond holding the atoms together in the
the van der Waals force increases with the increase in molecule. There are no ions present in liquid
the size of the hydrogen halide molecules as well as hydrogen chloride. As a result it does not
the number of electrons in the molecules from HCl conduct electricity.
to HI. This is reflected in the increase in the boiling However, when hydrogen chloride dissolves in
point from HCl to HI. HF, despite its smallest size has water it undergoes complete dissociation to
the highest boiling point. This is due to the presence produce free aqueous ions.
of hydrogen bonding between the HF molecules. HCl(g) + H O(l) → H O (aq) + Cl (aq)
–
+
2
3
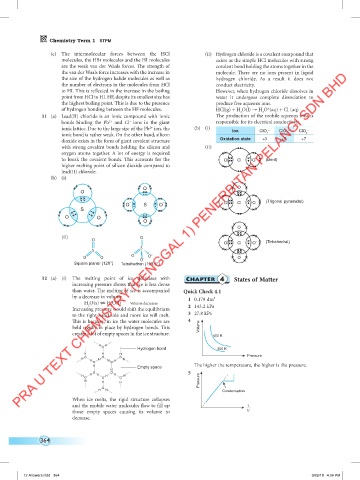
11 (a) Lead(II) chloride is an ionic compound with ionic The production of the mobile aqueous ions is
2+
–
bonds binding the Pb and Cl ions in the giant responsible for its electrical conductivity.
2+
ionic lattice. Due to the large size of the Pb ion, the (b) (i) Ion ClO – ClO – ClO –
ionic bond is rather weak. On the other hand, silicon 2 3 4
dioxide exists in the form of giant covalent structure Oxidation state +3 +5 +7
with strong covalent bonds holding the silicon and (ii)
oxygen atoms together. A lot of energy is required
to break the covalent bonds. This accounts for the O CI O – (Bent)
higher melting point of silicon dioxide compared to
lead(II) chloride.
(b) (i)
O O
O
O - S O - O CI O – (Trigonal pyramidal)
S
O O
O
O
(ii) O
O –
O CI O (Tetrahedral)
S
S
O O O O - O - O
Square planar (120°) Tetrahedron (109.5°)
12 (a) (i) The melting point of ice decreases with Chapter 4 States of Matter
increasing pressure shows that ice is less dense
than water. The melting of ice is accompanied Quick Check 4.1
by a decrease in volume. 1 0.179 dm
3
H O(s) H O(l) Volume decreases
2 2 2 143.2 kPa
Increasing pressure would shift the equilibrium
to the right-hand side and more ice will melt. 3 27.8 kPa
This is because, in ice the water molecules are 4
held rigidly in place by hydrogen bonds. This Volume
creates a lot of empty spaces in the ice structure.
400 K
H O H
Hydrogen bond 300 K
H H H
O O O Pressure
H H H
H H H
O O
H Empty space The higher the temperature, the higher is the pressure.
H
H O H O H 5
H H H
O O O
H H H Pressure
O
H H Condensation
When ice melts, the rigid structure collapses
and the mobile water molecules flow to fill up 1
those empty spaces causing its volume to V
decrease.
364
12 Answers.indd 364 3/26/18 4:06 PM