Page 33 - ACE YR IGCSE A TOP APPROACH TO CHEM
P. 33
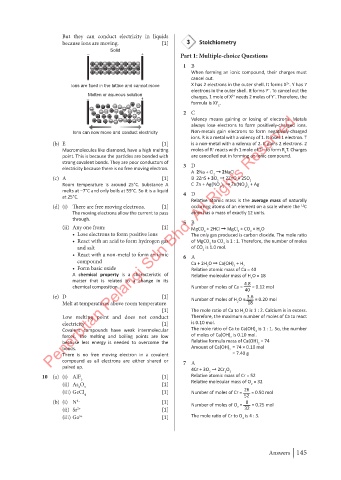
But they can conduct electricity in liquids
because ions are moving. [1] 3 Stoichiometry
Solid
– + Part 1: Multiple-choice Questions
+ – + – + – + – + – + – 1 B
– + – + – + – + – + – +
+ – + – + – + – + – + – When forming an ionic compound, their charges must
cancel out.
2+
Ions are fixed in the lattice and cannot move X has 2 electrons in the outer shell. It forms X . Y has 7
–
electrons in the outer shell. It forms Y . To cancel out the
Molten or aqueous solution 2+ –
– + charges, 1 mole of X needs 2 moles of Y . Therefore, the
formula is XY .
+ +
– + – – + – – – – + – – 2
–
Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn Bhd. All Rights Reserved.
+ + – – 2 C
+ + + + + + –
+ + + – – – – + – – Valency means gaining or losing of electrons. Metals
always lose electrons to form positively-charged ions.
Ions can now move and conduct electricity Non-metals gain electrons to form negatively-charged
ions. R is a metal with a valency of 1. It loses 1 electron. T
(b) E [1] is a non-metal with a valency of 2. It gains 2 electrons. 2
2–
+
Macromolecules like diamond, have a high melting moles of R reacts with 1 mole of T to form R T. Charges
2
point. This is because the particles are bonded with are cancelled out in forming an ionic compound.
strong covalent bonds. They are poor conductors of
electricity because there is no free moving electron. 3 D
A 2Na + Cl ➞ 2NaCl
2
(c) A [1] B 2ZnS + 3O ➞ 2ZnO + 2SO 2
2
Room temperature is around 25°C. Substance A C Zn + Ag(NO ) ➞ Zn(NO ) + Ag
3 2
3 2
melts at –7°C and only boils at 59°C. So it is a liquid
at 25°C. 4 D
Relative atomic mass is the average mass of naturally
(d) (i) There are free moving electrons. [1] occurring atoms of an element on a scale where the C
12
The moving electrons allow the current to pass atom has a mass of exactly 12 units.
through. 5 B
(ii) Any one from: [1] MgCO + 2HCl ➞ MgCl + CO + H O
2
3
2
2
• Lose electrons to form positive ions The only gas produced is carbon dioxide. The mole ratio
• React with an acid to form hydrogen gas of MgCO to CO is 1 : 1. Therefore, the number of moles
3
2
and salt of CO is 1.0 mol.
2
• React with a non-metal to form an ionic 6 A
compound Ca + 2H O ➞ Ca(OH) + H
2
2
2
• Form basic oxide Relative atomic mass of Ca = 40
A chemical property is a characteristic of Relative molecular mass of H O = 18
matter that is related to a change in its 4.8 2
chemical composition. Number of moles of Ca = = 0.12 mol
40
(e) D [1] Number of moles of H O = 3.6 = 0.20 mol
Melt at temperatures above room temperature 2 18
[1] The mole ratio of Ca to H O is 1 : 2. Calcium is in excess.
2
Low melting point and does not conduct Therefore, the maximum number of moles of Ca to react
electricity [1] is 0.10 mol.
Covalent compounds have weak intermolecular The mole ratio of Ca to Ca(OH) is 1 : 1. So, the number
2
forces. The melting and boiling points are low of moles of Ca(OH) is 0.10 mol.
2
because less energy is needed to overcome the Relative formula mass of Ca(OH) = 74
2
bonds. Amount of Ca(OH) = 74 × 0.10 mol
2
There is no free moving electron in a covalent = 7.40 g
compound as all electrons are either shared or 7 A
paired up.
4Cr + 3O ➞ 2Cr O 3
2
2
10 (a) (i) AlF [1] Relative atomic mass of Cr = 52
3 Relative molecular mass of O = 32
(ii) As O [1] 2
3
2
(iii) GeCl [1] Number of moles of Cr = 26 = 0.50 mol
4 52
(b) (i) N [1] Number of moles of O = 8 = 0.25 mol
3–
(ii) Sr [1] 2 32
2+
3+
(iii) Ga [1] The mole ratio of Cr to O is 4 : 3.
2
Answers 145
Answers.indd 145 3/4/22 3:54 PM