Page 9 - Top Class F5 - Mathematics (Chapter 2)
P. 9
Mathematics Form 5 Chapter 2 Matrices
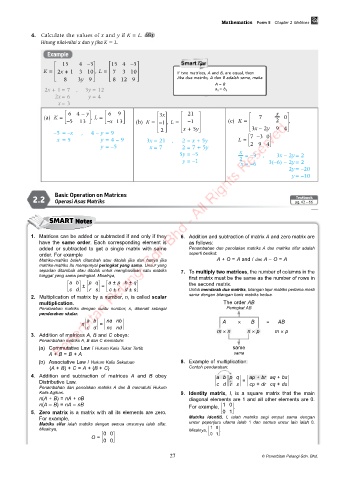
4. Calculate the values of x and y if K = L. PL 3
Hitung nilai-nilai x dan y jika K = L.
Example
15 4 –3 15 4 –3
K = 2x + 1 3 10 , L = 7 3 10 If two matrices, A and B, are equal, then
8 3y 9 8 12 9 Jika dua matriks, A dan B adalah sama, maka
A = B
2x + 1 = 7 , 3y = 12 a ij = b ij
2x = 6 y = 4
x = 3
6 4 – y 6 9 3x 21 x
(a) K = –5 13 , L = –x 13 (c) K = 7 2 0 ,
–1
(b) K = –1 , L =
2 x + 5y 3x – 2y 9 4
–5 = –x , 4 – y = 9
x = 5 y = 4 – 9 3x = 21 , 2 = x + 5y L = 7 –3 0
y = –5 x = 7 2 = 7 + 5y 2 9 4
5y = –5 x = –3 , 3x – 2y = 2
2
y = –1 x = –6 3(–6) – 2y = 2
2y = –20
y = –10
2.2 Basic Operation on Matrices pg. 42 – 66
Textbook
Operasi Asas Matriks
SMART Notes
1. Matrices can be added or subtracted if and only if they 6. Addition and subtraction of matrix A and zero matrix are
have the same order. Each corresponding element is as follows:
added or subtracted to get a single matrix with same Penambahan dan penolakan matriks A dan matriks sifar adalah
order. For example seperti berikut:
Matriks-matriks boleh ditambah atau ditolak jika dan hanya jika A + O = A and / dan A – O = A
matriks-matriks itu mempunyai peringkat yang sama. Unsur yang
sepadan ditambah atau ditolak untuk menghasilkan satu matriks 7. To multiply two matrices, the number of columns in the
tunggal yang sama peringkat. Misalnya, first matrix must be the same as the number of rows in
=
a b p q a ± p b ± q the second matrix.
±
c d
r s
c ± r d ± s
Untuk mendarab dua matriks, bilangan lajur matriks pertama mesti
2. Multiplication of matrix by a number, n, is called scalar sama dengan bilangan baris matriks kedua.
multiplication. The order AB
Pendaraban matriks dengan suatu nombor, n, dikenali sebagai Peringkat AB
pendaraban skalar.
=
n a b na nb A × B = AB
nc nd
c d
3. Addition of matrices A, B and C obeys: m × n n × p m × p
Penambahan matriks A, B dan C mematuhi:
(a) Commutative Law / Hukum Kalis Tukar Tertib same
A + B = B + A sama
(b) Associative Law / Hukum Kalis Sekutuan 8. Example of multiplication:
(A + B) + C = A + (B + C) Contoh pendaraban:
4. Addition and subtraction of matrices A and B obey a b p q ap + br aq + bs
=
Distributive Law. c d r s cp + dr cq + ds
Penambahan dan penolakan matriks A dan B mematuhi Hukum
Kalis Agihan. 9. Identity matrix, I, is a square matrix that the main
n(A + B) = nA + nB diagonal elements are 1 and all other elements are 0.
n(A – B) = nA – nB For example, 1 0 .
5. Zero matrix is a matrix with all its elements are zero. 0 1
For example, Matriks identiti, I, ialah matriks segi empat sama dengan
Matriks sifar ialah matriks dengan semua unsurnya ialah sifar. unsur pepenjuru utama ialah 1 dan semua unsur lain ialah 0.
1 0
Misalnya, Misalnya, .
O = 0 0 0 1
0 0
27 © Penerbitan Pelangi Sdn. Bhd.