Page 17 - Cambridge IGCSE Mathematics Core and Extended
P. 17
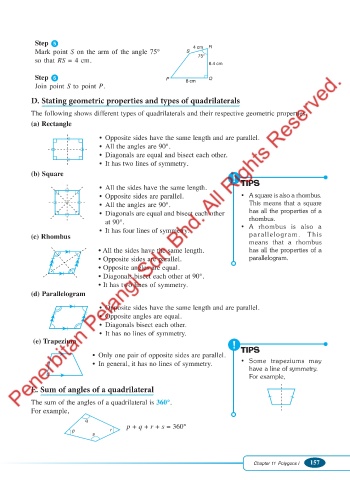
Step 5
4 cm R
Mark point S on the arm of the angle 75° S
75°
so that RS = 4 cm.
6.4 cm
Step 6 P 8 cm Q
Join point S to point P.
D. Stating geometric properties and types of quadrilaterals
The following shows different types of quadrilaterals and their respective geometric properties.
(a) Rectangle
• Opposite sides have the same length and are parallel.
• All the angles are 90°.
• Diagonals are equal and bisect each other.
• It has two lines of symmetry.
(b) Square
TIPS
• All the sides have the same length.
• Opposite sides are parallel. • A square is also a rhombus.
• All the angles are 90°. This means that a square
• Diagonals are equal and bisect each other has all the properties of a
rhombus.
at 90°. • A rhombus is also a
• It has four lines of symmetry.
(c) Rhombus parallelogram. This
means that a rhombus
• All the sides have the same length. has all the properties of a
• Opposite sides are parallel. parallelogram.
• Opposite angles are equal.
• Diagonals bisect each other at 90°.
• It has two lines of symmetry.
(d) Parallelogram
• Opposite sides have the same length and are parallel.
• Opposite angles are equal.
• Diagonals bisect each other.
• It has no lines of symmetry.
(e) Trapezium
TIPS
• Only one pair of opposite sides are parallel.
• In general, it has no lines of symmetry. • Some trapeziums may
have a line of symmetry.
For example,
E. Sum of angles of a quadrilateral
The sum of the angles of a quadrilateral is 360°.
For example,
q
p + q + r + s = 360°
p r
s
Chapter 11 Polygons I 157
14/07/2022 10:15 AM
DA1501_pg 147 to 161.indd 157
DA1501_pg 147 to 161.indd 157 14/07/2022 10:15 AM