Page 148 - Learn To Program With Scratch
P. 148
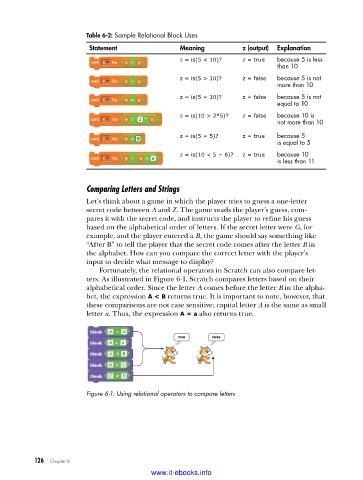
Table 6-2: Sample Relational Block Uses
Statement Meaning z (output) Explanation
z = is(5 < 10)? z = true because 5 is less
than 10
z = is(5 > 10)? z = false because 5 is not
more than 10
z = is(5 = 10)? z = false because 5 is not
equal to 10
z = is(10 > 2*5)? z = false because 10 is
not more than 10
z = is(5 = 5)? z = true because 5
is equal to 5
z = is(10 < 5 + 6)? z = true because 10
is less than 11
Comparing Letters and Strings
Let’s think about a game in which the player tries to guess a one-letter
secret code between A and Z. The game reads the player’s guess, com-
pares it with the secret code, and instructs the player to refine his guess
based on the alphabetical order of letters. If the secret letter were G, for
example, and the player entered a B, the game should say something like
“After B” to tell the player that the secret code comes after the letter B in
the alphabet. How can you compare the correct letter with the player’s
input to decide what message to display?
Fortunately, the relational operators in Scratch can also compare let-
ters. As illustrated in Figure 6-1, Scratch compares letters based on their
alphabetical order. Since the letter A comes before the letter B in the alpha-
bet, the expression A < B returns true. It is important to note, however, that
these comparisons are not case sensitive; capital letter A is the same as small
letter a. Thus, the expression A = a also returns true.
Figure 6-1: Using relational operators to compare letters
126 Chapter 6
www.it-ebooks.info