Page 130 - T-I JOURNAL19 4
P. 130
778 NNAKWE, COOCH & HUANG-SAAD INVESTING IN ACADEMIC TECHNOLOGY INNOVATION 779
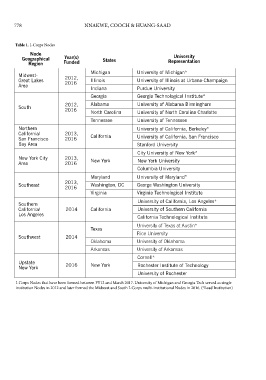
Table 1. I-Corps Nodes The University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, of I-Corps curricular concepts into undergraduate
the University of California at San Diego, the and graduate curriculum, thus broadening the impact
Node
University
Geographical Year(s) States Representation University of Akron, and the University of Toledo of I-Corps beyond individual teams (25).
Region Funded were the first four I-Corps Sites in 2013. Each institu-
Michigan University of Michigan* tion received $100,000 per year for a three-year term I-CORPS TO DATE
Midwest- 2012, (Table 2). Institutions that request and are awarded As of FY17, there are eight NSF I-Corps Nodes
Great Lakes 2016 Illinois University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign $100,000 per year are expected to support 30 local
Area (Table 1) and 67 I-Corps Sites (Table 2). An over-
Indiana Purdue University teams per year. The original solicitation was revised view of the timeline and evolution of the program
Georgia Georgia Technological Institute* and released in FY16 to extend the funding period is presented in Table 3. I-Corps Nodes are multi-in-
from three years to five years to provide sites the time
2012, Alabama University of Alabama Birmingham stitutional programs anchored in R1 institutions. At
South to formalize the program at their institutions. the onset of the program, University of Michigan and
2016
North Carolina University of North Carolina Charlotte I-Corps Sites teams tend to follow one of three
Tennessee University of Tennessee paths. A proportion of teams conduct preliminary Georgia Institute of Technology (the first two I-Corps
Nodes) were the only single-institution Nodes. Both
Northern University of California, Berkeley* customer discovery and recognize that their research institutions became multi-institutional Nodes when
California/ 2013, California products do not have a fit in the marketplace. Other their grants were renewed in 2016. I-Corps Site insti-
San Francisco 2016 University of California, San Francisco teams identify a fit in the marketplace and are imme-
Bay Area Stanford University diately able to attract funding for further development tutions vary from large public research institutions to
small liberal arts colleges having STEM departments.
City University of New York* to start companies or to license their products. For From the initial pilot on October 1, 2011, to the
New York City 2013, New York New York University example, PhotoniCare, Inc., from the University end of March 1, 2017, a total of 973 teams have par-
Area 2016 of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, created a medical
Columbia University device to assist doctors in the selection of antibiot- ticipated in the national I-Corps Teams program from
Maryland University of Maryland* ics by identifying ear infection bacterial strains and 222 universities in 46 states, resulting in the creation
2013, attracted $2 million in non-dilutive funding after of over 320 companies that have collectively raised
Southeast Washington, DC George Washington University
2016 participating in the University of Illinois I-Corps more than $83 million in follow-on funding (Figure
Virginia Virginia Technological Institute 1) (26,27).
Sites program. Other teams go on to participate in the
University of California, Los Angeles* national I-Corps program to explore additional cus- Given its early track record of success, the Obama
Southern Administration called for I-Corps to be scaled across
California/ 2014 California University of Southern California tomer segments and/or develop and vet a minimum all federal agencies. With this support, the budget
Los Angeles California Technological Institute viable product. As the program has continued to
grow, more national I-Corps Teams are coming from for the program grew to $30 million in FY16 from
University of Texas at Austin* I-Corps Sites institutions. As of March 1, 2017, the an initial investment of $1 million to fund the first
Texas
Rice University percentages of national teams coming from I-Corps pilot cohort I-Corps Teams (16,27).
Southwest 2014 As I-Corps continues to grow, the core curriculum
Oklahoma University of Oklahoma institutions include 29% from I-Corps Sites, 18% and structure is kept consistent across Nodes with the
Arkansas University of Arkansas from I-Corps Nodes institutions, and 11% have come oversight of the I-Corps faculty Kernel Committee,
from institutions that are both an I-Corps Node and
Cornell* Site (https://www.nsf.gov/awardsearch/ advanced- chaired by Engle. Representatives from each Node
Upstate 2016 New York Rochester Institute of Technology Search.jsp). sit on the committee and submit suggestions and
New York innovations to be addressed by the committee. The
University of Rochester I-Corps Sites institutions have benefited from
receiving an award in a number of ways. I-Corps committee is responsible for determining which
I-Corps Nodes that have been formed between FY12 and March 2017. University of Michigan and Georgia Tech served as single Sites institutions typically produce teams that mirror innovations should be widely adopted.
institution Nodes in 2012 and later formed the Midwest and South I-Corps multi-institutional Nodes in 2016. (*Lead Institution) the industries in their region (e.g., bio-pharmaceu- I-Corps teams are still the core of the I-Corps pro-
tical focus in San Diego or nursing in Milwaukee) gram. One significant change to the structure of the
and contribute to those ecosystems. I-Corps Sites team is who can fill the role of the PI. Initially, teams
institutions have credited their ability to attract addi- consisted of an EL, PI, and a BM, where the PI was
tional funding to expand infrastructure and activities the NSF-funded research scientist. Now, teams consist
from donors to their I-Corps Sites awards (Personal of an EL, a Technical Lead (TL), and a BM. The TL
communication, University of Chicago, University of can be an NSF-funded PI, a postdoctoral researcher
Illinois Urbana-Champaign, unreferenced). Finally, with deep technical knowledge, or an institutional
I- Corps Sites awards have catalyzed the integration representative who is able to be a designated PI.