Page 279 - MARSIUM'21 COMP OF PAPER
P. 279
quantitative metrics such as the number of likes, comments, shares, views, or followers as indicators of audiences' engagement level
(Voorveld et al., 2018). The crucial elements in engagement, as stated by Schaefers et al. (2021), are its repetitive manner, the incorporating
resources (e.g., time and effort spent by consumers), and the interactivity happening among consumers within a particular channel (e.g.,
amount and range of activities acted out on a social media platform) as it is fundamental to focus on consumers' engagement occurring by
use of social media platform in a brand-related context.
The behavior of ‘liking’ as engagement metrics imply consumer’s acceptance or satisfaction toward social media content (Moran et al.,
2020). Consumer comments when they have something to say in the social media community as a means to deliver their feelings or opinions
in which other users can access and see (Song et al., 2021). Meanwhile, user’s activity of sharing will result in the spreading of information
that perform as electronic word-of-mouth (eWOM) (Fu et al., 2017). Moreover, nowadays the features of ‘repost’ story in Instagram and
‘retweet’ another user’s tweet in Twitter also represent the metric of sharing. According to Muñoz-Expósito et al. (2017) regarding a metric
used to evaluate engagement in Twitter, researcher noted that from a behavioral approach, users should be involved through interaction with
the content to stimulate consumer engagement by following the approach provided by Kayser and Bierwisch (2016) of five main
functionalities for users to interact on Twitter such as tweets, retweets, messages, hashtags, and follower relations.
Recognizing the significance of social media in stimulating consumers’ engagement is essential since social media holds the power to help
brands in evolving its users from passive consumers to active consumers in the forms of creating and sharing content with the other online
users (Oh et al., 2016). The reason is that, marketers need to recognize types of consumers that have the tendency to actively engage with
brands on social media platforms (Wallace et al., 2014) and their motivations to do so (Muntinga et al., as cited in Schivinski, 2021).
2.4 CONCEPTUAL MODEL
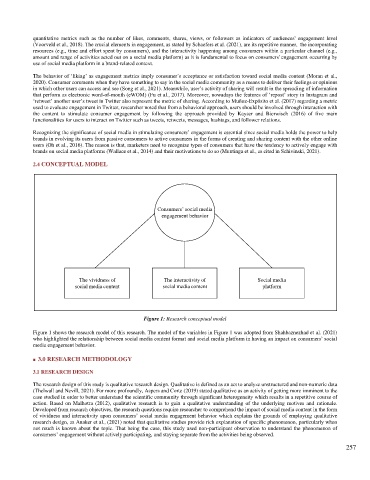
Consumers’ social media
engagement behavior
The vividness of The interactivity of Social media
social media content social media content platform
Figure 1: Research conceptual model
Figure 1 shows the research model of this research. The model of the variables in Figure 1 was adopted from Shahbaznezhad et al. (2021)
who highlighted the relationship between social media content format and social media platform in having an impact on consumers’ social
media engagement behavior.
■ 3.0 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3.1 RESEARCH DESIGN
The research design of this study is qualitative research design. Qualitative is defined as an act to analyze unstructured and non-numeric data
(Thelwall and Nevill, 2021). For more profoundly, Aspers and Corte (2019) stated qualitative as an activity of getting more imminent to the
case studied in order to better understand the scientific community through significant heterogeneity which results in a repetitive course of
action. Based on Malhotra (2012), qualitative research is to gain a qualitative understanding of the underlying motives and rationale.
Developed from research objectives, the research questions require researcher to comprehend the impact of social media content in the form
of vividness and interactivity upon consumers’ social media engagement behavior which explains the grounds of employing qualitative
research design, as Anaker et al., (2021) noted that qualitative studies provide rich explanation of specific phenomenon, particularly when
not much is known about the topic. That being the case, this study used non-participant observation to understand the phenomenon of
consumers’ engagement without actively participating, and staying separate from the activities being observed.
257