Page 377 - MARSIUM'21 COMP OF PAPER
P. 377
356 Leon (2021)
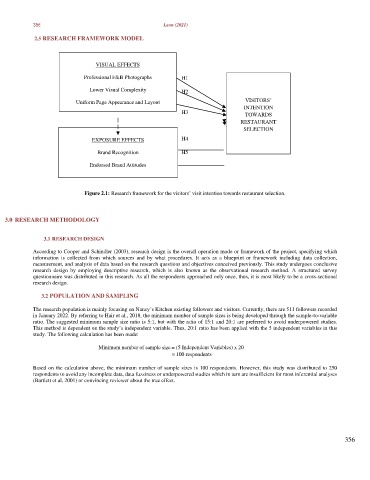
2.5 RESEARCH FRAMEWORK MODEL
VISUAL EFFECTS
Professional F&B Photographs H1
Lower Visual Complexity H2
Uniform Page Appearance and Layout VISITORS’
INTENTION
H3 TOWARDS
RESTAURANT
SELECTION
EXPOSURE EFFECTS H4
Brand Recognition H5
Endorsed Brand Attitudes
Figure 2.1: Research framework for the visitors’ visit intention towards restaurant selection.
3.0 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3.1 RESEARCH DESIGN
According to Cooper and Schindler (2003), research design is the overall operation mode or framework of the project, specifying which
information is collected from which sources and by what procedures. It acts as a blueprint or framework including data collection,
measurement, and analysis of data based on the research questions and objectives conceived previously. This study undergoes conclusive
research design by employing descriptive research, which is also known as the observational research method. A structured survey
questionnaire was distributed in this research. As all the respondents approached only once, thus, it is most likely to be a cross-sectional
research design.
3.2 POPULATION AND SAMPLING
The research population is mainly focusing on Nancy’s Kitchen existing followers and visitors. Currently, there are 511 followers recorded
in January 2022. By referring to Hair et al., 2018, the minimum number of sample sizes is being developed through the sample-to-variable
ratio. The suggested minimum sample size ratio is 5:1, but with the ratio of 15:1 and 20:1 are preferred to avoid underpowered studies.
This method is dependent on the study’s independent variable. Thus, 20:1 ratio has been applied with the 5 independent variables in this
study. The following calculation has been made:
Minimum number of sample size = (5 Independent Variables) x 20
= 100 respondents
Based on the calculation above, the minimum number of sample sizes is 100 respondents. However, this study was distributed to 250
respondents to avoid any incomplete data, data fuzziness or underpowered studies which in turn are insufficient for most inferential analyses
(Bartlett et al, 2001) or convincing reviewer about the true effect.
356