Page 478 - MARSIUM'21 COMP OF PAPER
P. 478
Muhamad Rifqi Zafran Bin Abdul Hakim (2022)
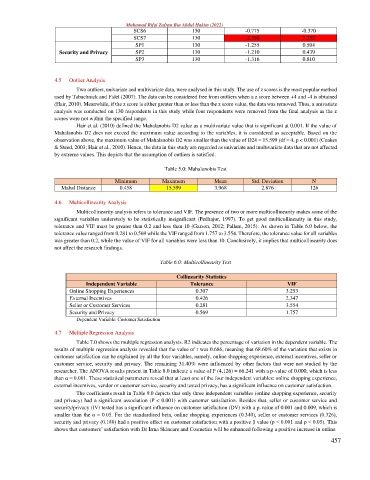
SCS6 130 -0.775 -0.370
SCS7 130 -2.350 7.352
SP1 130 -1.255 0.504
Security and Privacy SP2 130 -1.210 0.439
SP3 130 -1.316 0.810
4.5 Outlier Analysis
Two outliers, univariate and multivariate data, were analysed in this study. The use of z scores is the most popular method
used by Tabachnick and Fidel (2007). The data can be considered free from outliers when a z score between +4 and -4 is obtained
(Hair, 2010). Meanwhile, if the z score is either greater than or less than the z score value, the data was removed. Thus, a univariate
analysis was conducted on 130 respondents in this study while four respondents were removed from the final analysis as the z
scores were not within the specified range.
Hair et al. (2010) defined the Mahalanobis D2 value as a multivariate value that is significant at 0.001. If the value of
Mahalanobis D2 does not exceed the maximum value according to the variables, it is considered as acceptable. Based on the
observation above, the maximum value of Mahalanobis D2 was smaller than the value of D24 = 15.599 (df = 4, p < 0.001) (Coakes
& Steed, 2003; Hair et al., 2010). Hence, the data in this study are regarded as univariate and multivariate data that are not affected
by extreme values. This depicts that the assumption of outliers is satisfied.
Table 5.0: Mahalanobis Test
Minimum Maximum Mean Std. Deviation N
Mahal Distance 0.458 15.599 3.968 2.876 126
4.6 Multicollinearity Analysis
Multicollinearity analysis refers to tolerance and VIF. The presence of two or more multicollinearity makes some of the
significant variables understudy to be statistically insignificant (Pedhajur, 1997). To get good multicollinearity in this study,
tolerance and VIF must be greater than 0.2 and less than 10 (Garson, 2012; Pallant, 2015). As shown in Table 6.0 below, the
tolerance value ranged from 0.281 to 0.569 while the VIF ranged from 1.757 to 3.554. Therefore, the tolerance value for all variables
was greater than 0.2, while the value of VIF for all variables were less than 10. Conclusively, it implies that multicollinearity does
not affect the research findings.
Table 6.0: Multicollinearity Test
Collinearity Statistics
Independent Variable Tolerance VIF
Online Shopping Experiences 0.307 3.253
External Incentives 0.426 2.347
Seller or Customer Services 0.281 3.554
Security and Privacy 0.569 1.757
Dependent Variable: Customer Satisfaction
4.7 Multiple Regression Analysis
Table 7.0 shows the multiple regression analysis. R2 indicates the percentage of variation in the dependent variable. The
results of multiple regression analysis revealed that the value of r was 0.686, meaning that 68.60% of the variation that exists in
customer satisfaction can be explained by all the four variables, namely, online shopping experience, external incentives, seller or
customer service, security and privacy. The remaining 31.40% were influenced by other factors that were not studied by the
researcher. The ANOVA results present in Table 8.0 indicate a value of F (4,126) = 66.241 with a p-value of 0.000, which is less
than α = 0.001. These statistical parameters reveal that at least one of the four independent variables: online shopping experience,
external incentives, vendor or customer service, security and tested privacy, has a significant influence on customer satisfaction.
The coefficients result in Table 9.0 depicts that only three independent variables (online shopping experience, security
and privacy) had a significant association (P < 0.001) with customer satisfaction. Besides that, seller or customer service and
security/privacy (IV) tested has a significant influence on customer satisfaction (DV) with a p-value of 0.001 and 0.009, which is
smaller than the α = 0.05. For the standardised beta, online shopping experiences (0.340), seller or customer services (0.326),
security and privacy (0.180) had a positive effect on customer satisfaction with a positive β value (p < 0.001 and p < 0.05). This
shows that customers’ satisfaction with Dr Irma Skincare and Cosmetics will be enhanced following a positive increase in online
457