Page 250 - leadership-experience-2008
P. 250
CikguOnline
CikguOnline
CHAPTER 8: MOTIVATION AND EMPOWERMENT 231
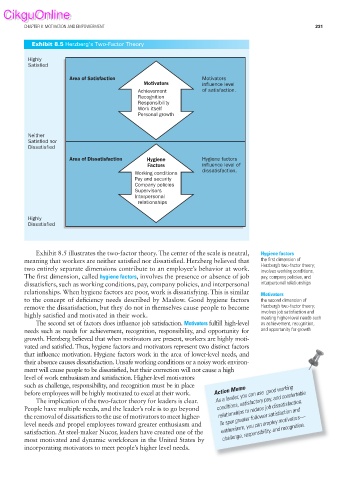
Exhibit 8.5 Herzberg’s Two-Factor Theory
Highly
Satisfied
Area of Satisfaction Motivators
Motivators influence level
Achievement of satisfaction.
Recognition
Responsibility
Work itself
Personal growth
Neither
Satisfied nor
Dissatisfied
Area of Dissatisfaction Hygiene Hygiene factors
Factors influence level of
dissatisfaction.
Working conditions
Pay and security
Company policies
Supervisors
Interpersonal
relationships
Highly
Dissatisfied
Exhibit 8.5 illustrates the two-factor theory. The center of the scale is neutral, Hygiene factors
Hygiene factors
the fi rst dimension of
meaning that workers are neither satisfi ed nor dissatisfied. Herzberg believed that the fi rst dimension of
Herzberg’s two-factor theory;
Herzberg’s two-factor theory;
two entirely separate dimensions contribute to an employee’s behavior at work.
involves working conditions,
involves working conditions,
The fi rst dimension, called hygiene factors, involves the presence or absence of job pay, company policies, and
pay, company policies, and
interpersonal relationships
dissatisfiers, such as working conditions, pay, company policies, and interpersonal interpersonal relationships
relationships. When hygiene factors are poor, work is dissatisfying. This is similar
Motivators
Motivators
to the concept of deficiency needs described by Maslow. Good hygiene factors the second dimension of
the second dimension of
Herzberg’s two-factor theory;
remove the dissatisfaction, but they do not in themselves cause people to become Herzberg’s two-factor theory;
involves job satisfaction and
involves job satisfaction and
highly satisfi ed and motivated in their work.
meeting higher-level needs such
meeting higher-level needs such
The second set of factors does influence job satisfaction. Motivators fulfi ll high-level as achievement, recognition,
as achievement, recognition,
and opportunity for growth
needs such as needs for achievement, recognition, responsibility, and opportunity for and opportunity for growth
growth. Herzberg believed that when motivators are present, workers are highly moti-
vated and satisfied. Thus, hygiene factors and motivators represent two distinct factors
that influence motivation. Hygiene factors work in the area of lower-level needs, and
their absence causes dissatisfaction. Unsafe working conditions or a noisy work environ-
ment will cause people to be dissatisfied, but their correction will not cause a high
level of work enthusiasm and satisfaction. Higher-level motivators
such as challenge, responsibility, and recognition must be in place
As a leader, you can use good working
before employees will be highly motivated to excel at their work. Action Memo
The implication of the two-factor theory for leaders is clear. conditions, satisfactory pay, and comfortable
People have multiple needs, and the leader’s role is to go beyond relationships to reduce job dissatisfaction.
the removal of dissatisfiers to the use of motivators to meet higher- To spur greater follower satisfaction and
level needs and propel employees toward greater enthusiasm and enthusiasm, you can employ motivators—
satisfaction. At steel-maker Nucor, leaders have created one of the challenge, responsibility, and recognition.
most motivated and dynamic workforces in the United States by
incorporating motivators to meet people’s higher level needs.